Superexchange coupling of donor qubits in silicon
Abstract
Atomic engineering in a solid-state material has the potential to functionalize the host with novel phenomena. STM-based lithographic techniques have enabled the placement of individual phosphorus atoms at selective lattice sites of silicon with atomic precision. Here, we show that by placing four phosphorus donors spaced 10-15 nm apart from their neighbours in a linear chain, it is possible to realize coherent spin coupling between the end dopants of the chain, analogous to the superexchange interaction in magnetic materials. Since phosphorus atoms are a promising building block of a silicon quantum computer, this enables spin coupling between their bound electrons beyond nearest neighbours, allowing the qubits to be spaced out by 30-45 nm. The added flexibility in architecture brought about by this long-range coupling not only reduces gate densities but can also reduce correlated noise between qubits from local noise sources that are detrimental to error correction codes. We base our calculations on a full configuration interaction technique in the atomistic tight-binding basis, solving the 4-electron problem exactly, over a domain of a million silicon atoms. Our calculations show that superexchange can be tuned electrically through gate voltages where it is less sensitive to charge noise and donor placement errors.
I Introduction
Donor qubits in silicon are promising candidates for encoding quantum information in the solid state due to their long coherence times [1, 2, 3] and their technological link to the silicon platform of the electronics industry. Experimental advancements in the past decades have enabled the precision placement of phosphorus donors in silicon [4, 5, 6, 7, 8]. The platform of phosphorus donor based quantum computing has been bolstered by key milestone achievements over the last decade, including single-shot spin-readout [9], the realization of single electron and nuclear spin qubits [10, 11], and more recently, two-qubit SWAP gates [12] and three-qubit donor quantum processor with universal logic operation [13]. Exchange coupling between the electronic spins of donors remains a key mechanism for fast coupling of two qubits [12, 14]. The exchange interaction depends on the overlap between the electronic wavefunctions and ultimately limits the separation of donor qubits to about 10-15 nm in silicon devices. Long-range coupling schemes through resonators and cavities have recently been explored in donor qubits [15, 16, 17], however, these typically require additional fabrication and integration steps adding complexity to the overall manufacturing process. Spacing out the qubits is beneficial from an architectural point of view in fault-tolerant quantum computing [18] as correlations between the qubits due to local noise sources can be minimised. An increase in separation also relaxes stringent gate density requirements and offers more independent electrostatic control of the qubits by reducing their capacitive cross-talk. For STM-patterned donors with phosphorus doped in-plane gates, the density is already low [19], so this technique is particularly appealing.
In this work, we study long-range exchange coupling between the end spins of four single donor (1P) quantum dots in a linear chain. With each donor containing a single electron, a superexchange coupling is found to emerge between the donors at the end of the chain. This third nearest neighbour interaction enables the qubits to be separated by 30-45 nm. Using atomistic full configuration interaction calculations, we study the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of four electron spins across four 1P atoms in silicon. We investigate the regime of superexchange where the distant qubits can be coherently manipulated and provide guidelines on the appropriate donor placement to achieve this. We also investigate the role of the conduction band valleys on superexchange for donor separation along different crystallographic directions. We simulate the system using realistic electrostatic potentials produced by the surrounding in-plane STM-patterned gates where we demonstrate tunability of superexchange with gate voltages, a crucial requirement for the realization of electrically-controlled singlet-triplet oscillations. Finally, we comment on the sensitivity of superexchange to charge noise and donor placement errors, as well as the role of nuclear spins in singlet-triplet oscillations induced by superexchange.

Recent experiments and theoretical calculations have shown indirect coupling of distant electrons in quantum dots via a central empty mediator [20, 21, 22, 23, 24], multi-electron quantum dot [21, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29] and linear chain of singly-occupied quantum dots [20, 30, 31]. However, to date, comprehensive studies have not been performed on long-range indirect coupling for donor qubits in silicon. Compared to electrostatically defined quantum dots, donor quantum dots in silicon typically have atomic-scale properties with wavefunction length scales an order of magnitude less and large quantity of orbital-valley energy splittings [32]. A single phosphorus donor can bind at most one or two electrons with the nucleus having a net spin. Early papers on single donor qubits showed how the exact position and axis of separation of donor qubits can significantly affect their direct exchange, including such effects as exchange oscillations due to valley interference [33, 34]. More recent work has shown that these effects can be mitigated by separating the donors along specific crystallographic directions, by using multi-donor quantum dots [35] or by applying strain or placing the donors close to the surface [33]. Highly tunable nearest-neighbour exchange has also been predicted [35] and demonstrated [12] in asymmetric donor quantum dots, showing that multi-electron molecular physics can be tuned by gate voltages. However, the atomistic character of these donors and donor dot systems needs to be accounted for when considering indirect couplings like superexchange since the phenomenon emerges from individual nearest-neighbour exchange couplings.
II Methods
The exact calculation of a multi-electron system is challenging because of the complicated and numerically intensive electron-electron interaction term in the Schrödinger equation [36]. The accuracy relies both on the quality of the basis states and the multi-electron approximation. In semiconductor materials such as GaAs, eigenstates from effective Hubbard Hamiltonian [20, 25, 37] or simple Fock-Darwin states are often used as basis states [21]. These are however unsuitable for silicon due to the multi-valley states. The effective mass approximation has also been used for calculating single electron basis states for donors in silicon [38, 39]. However, the theory does not provide a complete description of the band structure and can be inaccurate at higher energy levels. On the contrary, the full-band atomistic tight-binding model has the potential to capture all intricate nuances of the wavefunction of phosphorus donors in silicon hence its use in this work.
The most common approximation for multi-electron calculations is the Hartree-Fock method which neglects the electron-electron correlations to minimize the complexity of the calculations. Configuration interaction (CI), on the other hand, enhances the accuracy in the treatment of many-body interactions but can be computationally intensive. This is particularly true for a multi-valley material like silicon where only a few electron calculations are present in the literature [33, 40]. In this paper, we have performed state-of-the-art investigation combining atomistic basis states with a full configuration interaction method to calculate the energy levels of a four-electron donor system without compromising accuracy.
II.1 Atomistic Full Configuration Interaction
Full configuration interaction (FCI) is a method to obtain the exact numerical solution of a many-body Schrödinger equation, limited by the number and quality of single electron basis states. The single electron basis states used here are calculated using a 10-band atomistic tight-binding (TB) method in NEMO3D [41, 42]. This approach uses a localized atomic orbital-based method with nearest-neighbour interactions. The TB parameters are optimized to reproduce the bulk silicon band structure [43]. The phosphorus donors are represented using a Coulomb potential with a central cell correction at the donor site which can successfully determine the experimentally measured energy spectra of donors in silicon [44, 45].
The schematic representation of the simulations is illustrated in Figure 1(a). There are four phosphorus donors placed in a chain, each with an electron. The end electron spins, and are the qubits separated by R. The middle spins, and work as mediators with corresponding donors being separated by . The separation between and is and the separation between and is . The simulation domains used in the calculations entail million atoms which account for nm of silicon in the direction of separation and nm in the other two directions. The single electron basis states, solved from a parallel Block Lanczos eigensolver, are used to calculate the anti-symmetric Slater determinants of the multi-electron problem. The lowest two single electron valley-orbital states of the system are shown in Figure 1(b) and (c). Here we see bonding and anti-bonding state formation in the middle two donors and of a four-donor chain. The rest of the single electron molecular basis states are shown in Figure 8 in the Supplementary Information where we see the next two valley-orbital states are mainly localized in the outer donor dots.
The four-electron wavefunction is a superposition of various symmetry-permitted configurations of the Slater determinants. All possible integrals between the Slater Determinants with pairwise electronic interaction operators are computed to capture Coulomb, exchange, and higher-order correlations. The four electron Hamiltonian constructed from the Slater determinants is solved using the block Krylov-Schur algorithm within the Trilinos framework [46]. The number of single electron basis states in FCI calculations is increased until the eigenvalues of the four-electron system converge within a chosen tolerance – see Supplementary Information. On average, 56 single-electron basis states are sufficient to reach convergence. The eigenvalue of the ground state is separated from the triply degenerate excited states by the indirect exchange coupling. We place the donor atoms in different separations and orientations in our simulations and calculate this exchange coupling.
II.2 Effective spin Hamiltonian
To analyze and interpret our FCI results, we compare them with an effective Hamiltonian model [30]. We can represent the four-spin system with a spin Hamiltonian such as -
| (1) |
where is a Pauli matrix corresponding to an electron spin located on donor in the chain. is the exchange coupling between the middle two spins, and . is the exchange coupling between and and is the exchange coupling between and – see Figure 1(a) for the schematic of the system.
We only consider the subspace with spin-zero states () to construct the Hamiltonian as we are interested in the singlet-triplet oscillations in the qubits and . When , we can isolate the low energy states of the four-electron spin Hamiltonian using a Schrieffer-Wolff transformation. In that case, the effective Hamiltonian in a Heisenberg exchange form, [30] now becomes -
| (2) |
In the regime where , the lowest energy eigenstates are characterized by the singlet state formed within the two middle dots and singlet or triplet states formed within the outer dots [30]. The energy difference, between the lowest long-distance singlet and triplet states, i.e.
| (3) |
is what we call superexchange () in this paper – see Figure 3(a) for the energy level diagram of the system. For the middle-dot singlet manifold is well separated from all the middle-dot triplet states desirable for coherent coupling of the outer spins only, without any interference from the middle-dot spins.
III Results and Discussions
III.1 Equal nearest-neighbour separation of donors
We first analyze the equidistant case, where the separation between each neighbouring pair of donors is equal, – see Figure 1. Here we have approximately equal values of exchange coupling between each pair of donors, i.e. . In Figure 2 (with red dots), we show the values of the indirect exchange coupling for these equispaced donors (4P chain) with constant but increasing separation between the dots along the (left) and directions (right) in the silicon crystal, calculated using FCI. For comparison, we also plot (with blue dots) the direct exchange values for two donors, i.e. 1P-1P system, separated by R, as previously calculated in [35]. Looking at the fitted dashed lines between the 4P chain and 1P-1P cases, we can see that the presence of the mediator donors dramatically increases the exchange coupling between the two outer spins. The indirect exchange coupling for a donor chain of of about 25 nm reaches GHz ( meV), while for direct exchange for the same separation without the presence of mediators would fall below GHz ( meV) (extrapolated from the dataset in [35]).

We also see that the direct exchange decays much faster than the indirect exchange by comparing the slope of these two plots, true for both [100] and [110] crystal directions. For the [100] case in Figure 2(a), the slope of the fitted dashed line for the direct exchange as a function of qubit separation is /nm whereas the slope for the indirect exchange is /nm. Similarly in the [110] case in Figure 2(b), the slope of the fitted line for the direct exchange is /nm whereas the slope for the indirect exchange is /nm. In general, the indirect exchange decays almost three times less with donor separation than the direct exchange. This dependency with distance lets the qubits be far separated in the device and allows less correlated noise between them while maintaining strong spin coupling. Since the nearest neighbour exchange coupling has an exponential dependence with increasing separation of the donors, one might expect superexchange to change as an exponential function of – see Equation 2. On the contrary, the nearest neighbour exchange coupling changes as an exponential function of the qubit separation which results in a faster decay of direct exchange than the indirect one.
We observe no oscillations in the exchange coupling when the donors are separated in the [100] direction whilst we see oscillations in the exchange energy for separation in the [110] orientation, a signature of inter-valley quantum interference arising from the band structure of silicon [33, 35, 47].

III.2 Different regimes of superexchange from effective spin Hamiltonian
To obtain superexchange and coherent control between the electron spin qubits at the end of the chains and , it is essential that the middle spins and form a singlet-like state. Otherwise, there will be additional oscillations originating from the middle spins impeding coherent manipulation of the qubits. Thus we are looking for an operational regime where the ground state and the first excited state are well separated from the higher energy states in which the indirect coupling can be termed superexchange. In Figure 3(a) we plot the energies of all the eigenstates of the effective Hamiltonian as a function of varying from 0 to 1. When the outer spins are weakly coupled with the middle spins (), we see two clear branches of energy states separated by but the separation between the branches decreases as .
In Figure 3(b), we plot the energy difference between the two lowest states, as a function of as calculated from and . These two lowest states are the long-distance singlet and triplet states, namely and . Here we see that, in the regime where , the solutions from the effective spin and the Schrieffer-Wolff Hamiltonian are the same since the assumption of the transformation is valid here. As increases, the two solutions start to diverge suggesting the Schrieffer-Wolff transformation no longer holds. The lowest two energy states (spanned by and ) are no longer well separated from the excited states and there are now triplet-like admixtures in the singlet-like state of the middle two spins.
In Figure 3(c), we can see the contributions in the ground state of the inner-dot singlet states (i.e. and ) and inner-dot triplet states (all the remaining basis states). When (i.e. the equidistant case where all donors are equally separated), the inner-dot singlet and triplet contributions in are both approximately 50% and we no longer have a well-defined two-level system of and , but now have contributions from the four higher states shown in 3(a). As decreases, the contribution of the inner-dot singlet reaches more than where (shaded region). This regime can be considered as a threshold for coherent operation of the qubits. However, we note that the threshold we mention here () is not the upper limit of the coherent regime. The ratio should ideally be very close to .

III.3 Modulating superexchange by changing the middle donor separation
To explore the coherent-control regime of the 4-donor chain using our FCI calculations, we switch from the equidistant case discussed in Figure 2 to a chain with varied ratios, see Figure 4. Here, we present values of the indirect exchange coupling for chains oriented along the [100] and [110] direction in 4 (a), (b) respectively, as a function of middle donor separation while keeping the outer donor separation constant. The lower middle donor separation corresponds to a higher exchange coupling and lower and couplings, moving the system closer to the regime well described by the Schrieffer-Wolff approximation. In general, we see from Figure 4 that the exchange coupling exponentially decreases as we decrease the middle donor separation. The grey dashed line represents the separation where . The exchange coupling shows two different dependencies on either side of this point. The first is where the distance between the middle donors is smaller than the values of or and the second is where it is large. For donors separated along the [110] direction, we see clear oscillations in as a function of .
As we have discussed in the previous section the equidistant donor chain is not suitable for coherent manipulation of distant spins due to the admixture of states. The right side of the grey dashed line where is therefore not valid for operating qubits. To specify the limits of these different regimes, we use the values of direct exchange from the 1P-1P results in Ref. [35] to find and and the corresponding threshold. Decreasing the separation of the middle dots gives rise to a value of the superexchange that decreases exponentially while increasing the inner singlet contributions to the ground state – see Table 1 in the supplementary information. So there is a trade-off between the strength of coupling and operation fidelity. However, we see even small changes in the middle donor separation, of the order of 2 nm, can increase the inner singlet contributions to the ground state from to while keeping the value of superexchange still high enough ( MHz or meV) for use in realistic devices.
III.4 Electrical control of superexchange
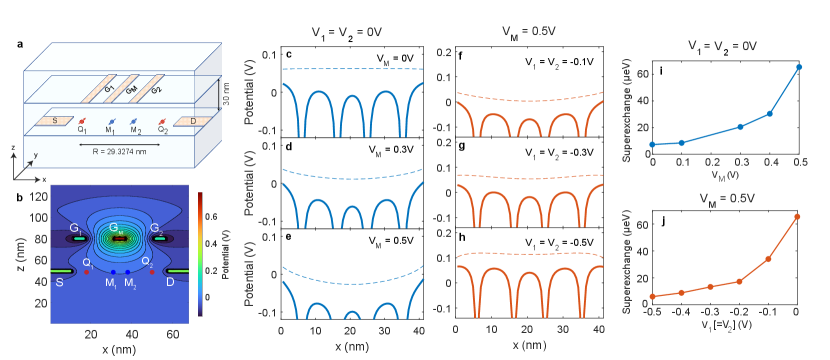
To address the tunability of superexchange, we have applied an electric field along the direction of the donor chain in our simulations where all donors are separated by nm ( = = = 9.7758 nm). For a realistic applied electric field of MV/m, we observe an exchange coupling of 18.09 GHz (eV) compared to 11.01 GHz (eV) under no electric field. The electric field detunes the qubits and increases the virtual tunnelling between them which results in slightly increased (less than a factor of 2) superexchange. However, when the donors are all charge neutral with one electron on each phosphorus atom, it is difficult to reach the (2,1,1,0) charge regime from a (1,1,1,1) regime without applying a very large bias. A similar challenge has been observed in [35] where applying an electric field of 2 MV/m the exchange coupling was modulated by 5 times. In the case of superexchange, the sensitivity of the coupling with an applied electric field is even less, hence, the distanced qubits are less susceptible to charge noise caused by electric field fluctuations compared to the nearest neighbour ones.
To explore different levels of control over superexchange, we apply a J-gate bias on a system with a
phosphorus-doped silicon top gate based on the original Kane architecture [14]. We place gates 30 nm above the donor plane to control the potential barrier between donor atoms and the nearest neighbour exchange and observe their effect on superexchange. Similar three-dimensional tuning of the potential barrier between in-plane phosphorus-doped gates has been recently experimentally demonstrated [48] in precision engineered STM tunnel junctions where the gates were degenerately phosphorus-doped silicon layers.
The schematic of the system is illustrated in Figure 5(a). The device consists of five quasi-metallic gates (source S, drain D, and three top gates - , and ). and are used to tune and and is used to tune . The total electrostatic potential profile of the device in the x-z plane is shown in Figure 5(b) where a cut is taken at the donor location. Here we see that, in the donor plane, the top gates create a parabolic potential profile. This total electrostatic potential is added to the tight-binding Hamiltonian while solving the energy levels of the donor quantum dots. In Figure 5(c-h), 1D cuts are taken at the donor locations shown for different and (=), i.e. for different voltages applied at gates and , respectively. Here S and D are grounded, i.e. . We note that just the presence of the electrostatic leads around the donors also modifies the total electrostatic potential of the device, even without an applied voltage. This is due to the band structure mismatch between the leads and the surrounding material, and the band-bending caused by the leads [49]. We calculate the total electrostatic potential profile of the device using a multi-scale modelling technique that combines the atomistic calculation of the band structure of the gates with a non-linear Poisson solution of the entire device [50].
III.4.1 Applying voltage to the middle top gate,
Since superexchange is a function of nearest-neighbour exchanges (i.e. , and ), it is necessary to understand how these exchange couplings change under an applied bias. When we apply a positive voltage to the middle gate , the potential barrier between the mediators and decreases but would increase - see Figure 5(c-e) for increasing values of . However, from the dashed line in Figure 5(e), we see that the applied bias in detunes the qubits and with respect to and so and would also increase. As we can see from Equation 2, the superexchange strongly depends on the interplay between and . In our case, here the superexchange increases overall with since the effect caused by detuning between the qubits and the mediator donors is stronger than from lowering the middle barrier – see the potential profile in Figure 5(e). We observe this effect on the value of in Figure 5(i), where we can see the superexchange as a function of for (case corresponding to 5(c-e)). By changing the middle gate potential from 0 to 0.5V, we modulate the magnitude of the superexchange by a factor of 10. The increase of superexchange is due to a relatively higher increase of than , resulting in lesser singlet contribution from the mediator dots, as discussed in the previous section. In our case, the singlet contribution in the middle dot drops from 92.2% () to 67% ().
III.4.2 Applying voltage to all three top gates, , and
We can minimize the detuning of the qubits and by applying a negative voltage to the left and right gates. Then the superexchange would decrease back - here from 65.42 eV to 6 eV when changing from 0 to -0.5 V for V – see Figure 5(j). The positive bias applied to increases and the negative bias applied to decreases , so the ratio becomes smaller. The potential profile at the donor location for and = = -0.1V, -0.3V and -0.5V is shown in Figure 5(f-h). If we look at the inner singlet contributions on the ground state, we see that the contribution has increased up to 94.05% when = = -0.5V. Tuning superexchange by using three gates might be useful in increasing the fidelity of the operation, otherwise, the tuning shows a similar range of superexchange even with one top gate. With these simulations, we have shown that it is possible to manipulate superexchange in a 4P chain by purely electrostatic means. Applying voltage through top gates exhibits better tunability of superexchange than a tilt voltage along the donor separation. We have shown that it is possible to modulate superexchange by a factor of 10 with modest gate potentials of 0.5 V. We note that even higher tunability might be desired to turn the coupling on and off for qubit operations. Such high tunability of the exchange coupling can also be achieved by depleting the middle donors. Without electrons in the middle donors, the qubits will be coupled by direct exchange which is significantly low at these separations. On the other hand, loading electrons in the middle donors will introduce a high value of superexchange. This mechanism can be crucial for the realization of singlet-triplet oscillations in distanced qubits.
III.5 Effect of asymmetric separation of the donors
Current STM lithography techniques allow us to place donor atoms in silicon with the precision of a single lattice constant [51, 52, 53, 54, 55]. As a consequence, we can investigate how small shifts in the exact P atom location within the four donor chain can affect the value of superexchange available. For that purpose, we analyze a chain oriented along the [100] direction with constant middle dot separation nm but with variable positions of the outer donors, described by and where 7 nm. We have deliberately chosen a smaller value of so that . We do not consider nearest neighbour separations less than 7 nm (qubit separation 20 nm) since we are interested in the long-distance qubit coupling regime and want to exceed the distance achievable by direct exchange.

The results are shown in Figure 6. Here we can see the superexchange is maximum (11.53 GHz) for the smallest values of and ( = = nm). This result arises both from minimizing the total chain separation, as well as maximizing the ratio – as observed in Figure 4. The value of decreases exponentially if either of the outer donors is moved outwards, i.e. if either or increases. However, at the same time, we can see does not change if both of the outer donors are shifted simultaneously in the same way – see the dashed lines where is constant. This result is consistent with the Schrieffer-Wolff approximation for superexchange in Eq. 2, where the dominating contribution to comes from . While and change approximately exponentially with distance, their product will not change when is kept constant.
Thus we can conclude that any small shifts in the location of the donors within the [100]-oriented chain can result in large changes in total . However, interestingly, a simultaneous shift of both outer (or both middle) donors in the same direction would not have any impact on the superexchange (indicated by the black dashed lines). The situation is completely different for the [110] crystalline direction due to the oscillations of two-donor exchange with distance which lifts the smooth dependency for varied when is constant. Here will change in an oscillatory manner if one or both middle donors are shifted.
III.6 Impact of donor nuclear spins on the superexchange
Finally, we comment on the presence of nuclear spins in the donor system and how they can also impact superexchange and coherent electron spin manipulation. The nuclear spins of phosphorus donor atoms couple with their electron spins through the hyperfine interaction. From the perspective of the electron spin, this can be treated as a small additional magnetic field dependent on the nuclear spin polarization. In the case of an electron singlet-triplet spin qubit, localized within the middle double donor dot, this hyperfine interaction can create a magnetic field gradient that mixes singlet and triplet states [17, 56]. For a 1P-1P system, the gradient is few Milli Tesla which gives rise to a Zeeman energy difference, meV between the donors when the two nuclear spins are oriented antiparallel () and when the two nuclear spins are aligned in the same direction ().
To create well-defined eigenstates as well as singlet and triplet states, the exchange coupling needs to dominate over . We can consider the 4-electron system discussed in this paper essentially as two pairs of singlet-triplet qubits – one defined between the two inner dots and one between the two outer dots. To avoid mixing of the singlet and triplet states it is desirable for both and to be significantly greater than . From Figure 2 this is satisfied when the middle donor separation is smaller than 10-15 nm, which includes most of the results presented in this work. The value of superexchange ultimately depends both on and . From Figure 4 we can see it is possible to design 4P configurations which belong to the regime where and at the same time satisfy . These considerations are however no longer relevant if we deterministically initialize the nuclear spins to all-parallel before any operation using a local Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) [10]. In this case, there is no magnetic field gradient and thus no limitations on the minimum values of and .
IV Conclusion
In this work, we have presented the results of strong non-nearest neighbour exchange coupling over a long distance (20-35 nm) with a possible extension of up to 45 nm, which has not been explored in donor quantum dots before. Using an atomistic full configuration interaction technique, we have calculated the eigenvalues of a 4-electron system with high-quality atomistic basis states and showed a comparison with an effective spin Hamiltonian to determine the viability of our intensive numerical calculations. We have shown that by placing the mediator donors one atomic position inwards compared to the symmetric chain, it is possible to enable coherent control of the qubits separated in [100] and [110] directions. Similarly to previous works on direct exchange, we observe a monotonic dependence of superexchange versus distance for donors separated in [100] and oscillatory dependence in [110]. Importantly, we demonstrate that the superexchange can be modulated by an order of magnitude by purely electrostatic means using realistic experimental gate voltages. These results pave the way for the realization of fast singlet-triplet control for distanced qubits. The calculations support the experimental realization of long-distance coupling of donor qubits in silicon.
References
- Muhonen et al. [2014] J. T. Muhonen, J. P. Dehollain, A. Laucht, F. E. Hudson, R. Kalra, T. Sekiguchi, K. M. Itoh, D. N. Jamieson, J. C. McCallum, A. S. Dzurak, and A. Morello, Nature Nanotechnology 9, 986 (2014).
- Steger et al. [2012] M. Steger, K. Saeedi, M. L. W. Thewalt, J. J. L. Morton, H. Riemann, N. V. Abrosimov, P. Becker, and H.-J. Pohl, Science 336, 1280 (2012).
- Tyryshkin et al. [2012] A. M. Tyryshkin, S. Tojo, J. J. L. Morton, H. Riemann, N. V. Abrosimov, P. Becker, H.-J. Pohl, T. Schenkel, M. L. W. Thewalt, K. M. Itoh, and S. A. Lyon, Nature Materials 11, 143 (2012).
- Schofield et al. [2003] S. R. Schofield, N. J. Curson, M. Y. Simmons, F. J. Rueß, T. Hallam, L. Oberbeck, and R. G. Clark, Physical Review Letters 91, 136104 (2003).
- Clark et al. [2003] R. G. Clark, R. Brenner, T. M. Buehler, V. Chan, N. J. Curson, A. S. Dzurak, E. Gauja, H. S. Goan, A. D. Greentree, T. Hallam, A. R. Hamilton, L. C. L. Hollenberg, D. N. Jamieson, J. C. McCallum, G. J. Milburn, J. L. O’Brien, L. Oberbeck, C. I. Pakes, S. D. Prawer, D. J. Reilly, F. J. Ruess, S. R. Schofield, M. Y. Simmons, F. E. Stanley, R. P. Starrett, C. Wellard, and C. Yang, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 361, 1451 (2003).
- Simmons et al. [2005] M. Simmons, F. Ruess, K. Goh, T. Hallam, S. Schofield, L. Oberbeck, N. Curson, A. Hamilton, M. Butcher, R. Clark, and T. Reusch, Molecular Simulation 31, 505 (2005).
- Rueß et al. [2007] F. J. Rueß, W. Pok, T. C. G. Reusch, M. J. Butcher, K. E. J. Goh, L. Oberbeck, G. Scappucci, A. R. Hamilton, and M. Y. Simmons, Small 3, 563 (2007).
- Fuechsle et al. [2012a] M. Fuechsle, J. A. Miwa, S. Mahapatra, H. Ryu, S. Lee, O. Warschkow, L. C. L. Hollenberg, G. Klimeck, and M. Y. Simmons, Nature Nanotechnology 7, 242 (2012a).
- Morello et al. [2010] A. Morello, J. J. Pla, F. A. Zwanenburg, K. W. Chan, K. Y. Tan, H. Huebl, M. Möttönen, C. D. Nugroho, C. Yang, J. A. van Donkelaar, A. D. C. Alves, D. N. Jamieson, C. C. Escott, L. C. L. Hollenberg, R. G. Clark, and A. S. Dzurak, Nature 467, 687 (2010).
- Pla et al. [2012] J. J. Pla, K. Y. Tan, J. P. Dehollain, W. H. Lim, J. J. L. Morton, D. N. Jamieson, A. S. Dzurak, and A. Morello, Nature 489, 541 (2012).
- Pla et al. [2013] J. J. Pla, K. Y. Tan, J. P. Dehollain, W. H. Lim, J. J. L. Morton, F. A. Zwanenburg, D. N. Jamieson, A. S. Dzurak, and A. Morello, Nature 496, 334 (2013).
- He et al. [2019] Y. He, S. K. Gorman, D. Keith, L. Kranz, J. G. Keizer, and M. Y. Simmons, Nature 571, 371 (2019).
- Mądzik et al. [2022] M. T. Mądzik, S. Asaad, A. Youssry, B. Joecker, K. M. Rudinger, E. Nielsen, K. C. Young, T. J. Proctor, A. D. Baczewski, A. Laucht, V. Schmitt, F. E. Hudson, K. M. Itoh, A. M. Jakob, B. C. Johnson, D. N. Jamieson, A. S. Dzurak, C. Ferrie, R. Blume-Kohout, and A. Morello, Nature 601, 348 (2022).
- Kane [1998] B. E. Kane, Nature 393, 133 (1998).
- Tosi et al. [2017] G. Tosi, F. A. Mohiyaddin, V. Schmitt, S. Tenberg, R. Rahman, G. Klimeck, and A. Morello, Nature Communications 8, 450 (2017).
- Morse et al. [2017] K. J. Morse, R. J. S. Abraham, A. DeAbreu, C. Bowness, T. S. Richards, H. Riemann, N. V. Abrosimov, P. Becker, H.-J. Pohl, M. L. W. Thewalt, and S. Simmons, Science Advances 3, e1700930 (2017).
- Osika et al. [2022] E. N. Osika, S. K. Gorman, S. Monir, Y.-L. Hsueh, M. Borscz, H. Geng, B. Thorgrimsson, M. Y. Simmons, and R. Rahman, Phys. Rev. B 106, 075418 (2022).
- Vandersypen et al. [2017] L. M. K. Vandersypen, H. Bluhm, J. S. Clarke, A. S. Dzurak, R. Ishihara, A. Morello, D. J. Reilly, L. R. Schreiber, and M. Veldhorst, npj Quantum Information 3, 1 (2017).
- Kiczynski et al. [2022] M. Kiczynski, S. K. Gorman, H. Geng, M. B. Donnelly, Y. Chung, Y. He, J. G. Keizer, and M. Y. Simmons, Nature 606, 694 (2022).
- Chan et al. [2021] K. W. Chan, H. Sahasrabudhe, W. Huang, Y. Wang, H. C. Yang, M. Veldhorst, J. C. C. Hwang, F. A. Mohiyaddin, F. E. Hudson, K. M. Itoh, A. Saraiva, A. Morello, A. Laucht, R. Rahman, and A. S. Dzurak, Nano Letters 21, 1517 (2021).
- Deng and Barnes [2020] K. Deng and E. Barnes, Phys. Rev. B 102, 035427 (2020).
- Rančić and Burkard [2017] M. J. Rančić and G. Burkard, Physical Review B 96, 201304 (2017).
- Baart et al. [2017] T. A. Baart, T. Fujita, C. Reichl, W. Wegscheider, and L. M. K. Vandersypen, Nature Nanotechnology 12, 26 (2017).
- Mehl et al. [2014] S. Mehl, H. Bluhm, and D. P. DiVincenzo, Physical Review B 90, 045404 (2014).
- Malinowski et al. [2019] F. K. Malinowski, F. Martins, T. B. Smith, S. D. Bartlett, A. C. Doherty, P. D. Nissen, S. Fallahi, G. C. Gardner, M. J. Manfra, C. M. Marcus, and F. Kuemmeth, Nature Communications 10, 1196 (2019).
- Malinowski et al. [2018] F. K. Malinowski, F. Martins, T. B. Smith, S. D. Bartlett, A. C. Doherty, P. D. Nissen, S. Fallahi, G. C. Gardner, M. J. Manfra, C. M. Marcus, and F. Kuemmeth, Physical Review X 8, 011045 (2018).
- Deng et al. [2018] K. Deng, F. A. Calderon-Vargas, N. J. Mayhall, and E. Barnes, Physical Review B 97, 245301 (2018).
- Croot et al. [2018] X. Croot, S. Pauka, J. Watson, G. Gardner, S. Fallahi, M. Manfra, and D. Reilly, Physical Review Applied 10, 044058 (2018).
- Srinivasa et al. [2015] V. Srinivasa, H. Xu, and J. Taylor, Physical Review Letters 114, 226803 (2015).
- Qiao et al. [2021] H. Qiao, Y. P. Kandel, S. Fallahi, G. C. Gardner, M. J. Manfra, X. Hu, and J. M. Nichol, Physical Review Letters 126, 017701 (2021).
- Fei et al. [2012] J. Fei, D. Zhou, Y.-P. Shim, S. Oh, X. Hu, and M. Friesen, Physical Review A 86, 062328 (2012).
- Ramdas and Rodriguez [1981] A. K. Ramdas and S. Rodriguez, Reports on Progress in Physics 44, 1297 (1981).
- Tankasala et al. [2022] A. Tankasala, B. Voisin, Z. Kembrey, J. Salfi, Y.-L. Hsueh, E. N. Osika, S. Rogge, and R. Rahman, Physical Review B 105, 155158 (2022).
- Voisin et al. [2020] B. Voisin, J. Bocquel, A. Tankasala, M. Usman, J. Salfi, R. Rahman, M. Y. Simmons, L. C. L. Hollenberg, and S. Rogge, Nature communications 11, 1 (2020).
- Wang et al. [2016] Y. Wang, A. Tankasala, L. C. L. Hollenberg, G. Klimeck, M. Y. Simmons, and R. Rahman, npj Quantum Information 2, 1 (2016).
- Szabo and Ostlund [1996] A. Szabo and N. S. Ostlund, Modern Quantum Chemistry: Introduction to Advanced Electronic Structure Theory (Dover Publications, 1996).
- Chan and Wang [2022] G. X. Chan and X. Wang, Physical Review A 106, 022420 (2022).
- Saraiva et al. [2015] A. L. Saraiva, A. Baena, M. J. Calderón, and B. Koiller, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 27, 154208 (2015).
- Joecker et al. [2021] B. Joecker, A. D. Baczewski, J. K. Gamble, J. J. Pla, A. Saraiva, and A. Morello, New Journal of Physics 23, 073007 (2021).
- Tankasala et al. [2018] A. Tankasala, J. Salfi, J. Bocquel, B. Voisin, M. Usman, G. Klimeck, M. Y. Simmons, L. C. L. Hollenberg, S. Rogge, and R. Rahman, Physical Review B 97, 195301 (2018).
- Ahmed et al. [2009] S. Ahmed, N. Kharche, R. Rahman, M. Usman, S. Lee, H. Ryu, H. Bae, S. Clark, B. Haley, M. Naumov, F. Saied, M. Korkusinski, R. Kennel, M. McLennan, T. B. Boykin, and G. Klimeck, Multimillion Atom Simulations with NEMO 3-D (2009), arXiv:0901.1890 [physics] .
- Klimeck et al. [2007] G. Klimeck, S. Ahmed, H. Bae, N. Kharche, S. Clark, B. Haley, S. Lee, M. Naumov, H. Ryu, F. Saied, M. Prada, M. Korkusinski, T. Boykin, and R. Rahman, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 54, 2079 (2007).
- Boykin et al. [2004] T. B. Boykin, G. Klimeck, and F. Oyafuso, Physical Review B 69, 115201 (2004).
- Rahman et al. [2007] R. Rahman, C. J. Wellard, F. R. Bradbury, M. Prada, J. H. Cole, G. Klimeck, and L. C. L. Hollenberg, Physical Review Letters 99, 036403 (2007).
- Rahman et al. [2009] R. Rahman, G. P. Lansbergen, S. H. Park, J. Verduijn, G. Klimeck, S. Rogge, and L. C. L. Hollenberg, Physical Review B 80, 165314 (2009).
- Baker et al. [2009] C. G. Baker, U. L. Hetmaniuk, R. B. Lehoucq, and H. K. Thornquist, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 36, 1 (2009).
- Koiller et al. [2001] B. Koiller, X. Hu, and S. D. Sarma, Physical Review Letters 88, 027903 (2001), arXiv:cond-mat/0106259 .
- Donnelly et al. [2021] M. B. Donnelly, J. G. Keizer, Y. Chung, and M. Y. Simmons, Nano Letters 21, 10092 (2021).
- Ryu et al. [2013] H. Ryu, S. Lee, B. Weber, S. Mahapatra, L. C. Hollenberg, M. Y. Simmons, and G. Klimeck, Nanoscale 5, 8666 (2013).
- Donnelly et al. [2023] M. B. Donnelly, M. M. Munia, J. G. Keizer, Y. Chung, A. S.-E. Huq, E. N. Osika, Y.-L. Hsueh, R. Rahman, and M. Y. Simmons, Advanced Functional Materials , 2214011 (2023).
- Fuechsle et al. [2012b] M. Fuechsle, J. A. Miwa, S. Mahapatra, H. Ryu, S. Lee, O. Warschkow, L. C. Hollenberg, G. Klimeck, and M. Y. Simmons, Nature nanotechnology 7, 242 (2012b).
- Ivie et al. [2021] J. A. Ivie, Q. Campbell, J. C. Koepke, M. I. Brickson, P. A. Schultz, R. P. Muller, A. M. Mounce, D. R. Ward, M. S. Carroll, E. Bussmann, A. D. Baczewski, and S. Misra, Phys. Rev. Appl. 16, 054037 (2021).
- Bussmann et al. [2021] E. Bussmann, R. E. Butera, J. H. Owen, J. N. Randall, S. M. Rinaldi, A. D. Baczewski, and S. Misra, MRS Bulletin 46, 607 (2021).
- Simmons and Keizer [2022] M. Y. Simmons and J. Keizer, U.S. Patent , US 11227768 B2 (2022).
- Wyrick et al. [2022] J. Wyrick, X. Wang, P. Namboodiri, R. V. Kashid, F. Fei, J. Fox, and R. Silver, ACS Nano 16, 19114 (2022).
- Kranz et al. [2022] L. Kranz, S. K. Gorman, B. Thorgrimsson, S. Monir, Y. He, D. Keith, K. Charde, J. G. Keizer, R. Rahman, and M. Y. Simmons, Advanced Materials , 2201625 (2022).
Appendix A Convergence of multi-electron states
The convergence of multi-electron states calculated using FCI depends on the number of single-electron states taken into the basis. As in this work, we investigate the effect of superexchange, i.e. the energy difference between outer-dot singlet and triplet states, and respectively, we use also to determine the convergence of our calculated four-electron states. We gradually increase the number of single-electron basis states in FCI calculations and observe when the changes in are negligible within some numerical tolerance. In Figure 7 we show examples of such analysis for donors separated in both [100] and [110] crystal directions. We find that in most of the cases considered in the paper, it is sufficient to use 56 basis states, i.e. 28 valley-orbital states, with two-fold spin degeneracy. In a few cases, we have used up to 72 basis states to reach convergence in the energy difference.

Appendix B Analysis of four-electron eigenstates

In this section, we analyze the 4-electron states in terms of their contributions from different Slater determinants, i.e. consisting of different 1-electron atomistic tight-binding basis states. This will help us to determine the regimes of where the eigenstates can be confidently described in terms of singlet-triplet symmetries. First, we focus on [100] crystal direction and the equidistant case . In Figure 8 we plot several of the lowest-energy single electron states.
-
•
We can see that the ground and first-excited orbitals (states numbered 1 and 3 in the figure) are localized mainly in the two middle dots. This is because superposing the four donors confining potentials in TB calculations results in the total potential being slightly deeper within the middle dots than the outer ones.
-
•
The next two excited orbitals (states 5 and 7) are localized mainly within two outer dots.
-
•
We consider the even-numbered states (2,4,6,8…) to be of the same orbital as odd (1,3,5,7…) but of opposite spin.
-
•
The 4-electron ground state, labelled by us as , has main contributions from following configurations: 14.7% , 14.7% , 10.7% , 9.5% , 8.9% , 7.8% , and smaller contributions from other configurations.
-
•
The first two contributions can be interpreted as inner-triplet outer-triplet states ( is in inner dots and in outer dots, is opposite to that).
-
•
Other configurations are inner-singlet outer-singlet states.
-
•
We can then see that a significant part of the ground state is described as an inner-dot triplet, which is specific for regime and has been expected by us following the above discussion on effective Hamiltonian states.
-
•
To obtain a rough estimate of the percentage of singlet and triplet contributions within the middle dots we sum up contributions from states for singlet and , , for triplet.
We show the results in Table 1. As expected from the effective Hamiltonian model here both contributions are close to 50%. The presented numbers are, however, just an estimate, not a precise evaluation of singlet and triplet admixtures in the middle dots as i) we do not sum up all the higher-order Slater determinant probabilities and ii) the orbitals 1 and 3 have small but non-zero probabilities also in the outer dots.
Next, we look at the non-equidistant case, with which guarantees . In Table 1 we compare inner-singlet and inner-triplet contributions in for 3 values of , i.e. , and , while keeping the total four-donor separation constant at . We can see the inner-singlet (inner-triplet) contribution is significantly increasing (decreasing) when the middle donors are pulled closer together.
| Separation () | Inner singlet contribution | Inner triplet contribution |
|---|---|---|
| 18 | 0.4927 | 0.483 |
| 16 | 0.9209 | 0.06706 |
| 14 | 0.97904 | 0.00238 |