Efficient LOCC extraction of quantum information encoded in stabilizer codes
Abstract
We construct a protocol for extracting distributed single-qubit quantum information encoded in a stabilizer code of multiple qubits, only by single-qubit local operations and classical communication (LOCC) without global operations or entanglement resources. This protocol achieves efficient extraction within a polynomial time in terms of the number of physical qubits. We apply this protocol to a setting of quantum information splitting where a subset of spatially separated parties cooperate by classical communication to extract quantum information shared among all the parties. For this task, our LOCC extraction protocol allows designing hierarchical information access structures among the parties, where the minimum number of parties required to cooperate depends on the location of extracting the shared quantum information. Extraction of quantum information encoded in the stabilizer code appears widely in distributed quantum information processing, such as quantum secret sharing. Our results allow such distributed quantum information processing without entanglement costs.
I Introduction
Connecting multiple quantum computers by classical and quantum communication channels enables various types of distributed quantum tasks [1, 2], such as quantum secret sharing [3, 4, 5]. In general, distributed quantum tasks require global quantum operation between distant quantum computers. Such global quantum operations are implemented by two-qubit gates across the distant qubits. To perform global two-qubit gates, one has to implement (or simulate) quantum communication between the qubits in different quantum computers, for example, by coherently transporting physical qubits [6] or by consuming preshared entanglement resources [7, 8, 9, 10, 11]. However, such quantum communication is costly to realize especially when quantum computers to be connected are further apart from each other.
For the cases that quantum communication should be avoided as much as possible, it is important to understand what kind of quantum tasks are still achievable without quantum communication. The class of quantum operations implementable without quantum communication is called local operations and classical communication (LOCC) [12, 13, 14] and played a fundamental role in the development of entanglement theory [15, 16, 13]. There are some cases where distributed quantum tasks are achievable only by LOCC, such as distinguishing quantum states by LOCC [17, 18] and recovering shared classical information by LOCC [19, 20, 21]. These tasks aim to extract classical information encoded in a quantum state.
In this paper, we analyze a quantum task to extract single-qubit quantum information distributed among multiple qubits to one of the qubits when we introduce parties each of whom holds only one qubit and can perform LOCC on each qubit [22, 23]. In this task, single-qubit quantum information is represented by an unknown single-qubit state and distributed among multiple qubits as a quantum state , where and are mutually orthogonal quantum states of the multiple qubits distributed to the parties. Extracting quantum information to a party is defined as a decoding transformation from a quantum state on the multiple qubits to a single-qubit state on a qubit at one of the parties. For example, recovering quantum information in the quantum secret sharing [3, 4, 5] and decoding of the quantum codes [24, 25, 26] can be considered as extracting quantum information.
Quantum information encoded in the generic quantum codes cannot be extracted only by LOCC without entanglement resources in general [23, 22, 27]. However, there are several individual examples where extraction is possible only by LOCC. If the logical basis is represented by particular graph states, it has been already known how to extract quantum information by LOCC as a part of the protocol of quantum secret sharing [28, 29, 30, 31]. There are also cases where extraction is possible without entanglement resources but it requires two-way LOCC [27, 32].
We provide a class of cases where LOCC extraction is possible, rather than individual examples by proving that single-qubit quantum information encoded in the stabilizer codes can always be extracted to one of the parties only by LOCC. We construct a protocol to extract single-qubit quantum information to an assigned party with one-way LOCC without entanglement resources when quantum information is encoded in stabilizer codes. Our algorithm to find such a protocol is based on a graph-theoretical representation of the decoding operations using graph states [33]. This algorithm works efficiently within a polynomial time in terms of the number of qubits, due to the efficiency of transforming the graphs.
We further investigate the minimum number of cooperative parties required for LOCC extraction of quantum information encoded in stabilizer codes. In general, some of the parties do not have to be cooperative; that is, LOCC involved only by a cooperative subset of the parties can achieve extraction of quantum information, irrespective to local operations performed by the other uncooperative parties. We find a type of stabilizer codes where the minimum required number of cooperative parties for extraction can be identified. The number of parties that need to cooperate for extraction depends on the assignment of the party to which the information is extracted. The difference in the minimum number of parties for extraction implies a hierarchical structure of distributing quantum information. The larger minimum number of parties indicates quantum information is “more non-locally distributed” as it requires the cooperation of more parties.
This hierarchical structure can be applied to construct a particular type of quantum information splitting (QIS) [34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 29, 31, 30]. The QIS is a technique for sharing quantum information among multiple parties. We consider a type of QIS where the parties cannot perform quantum communication, and the quantum information has to be recovered only with LOCC, which we call LOCC-QIS. In the QIS shown in Refs. [29, 30, 31], the hierarchical structures of authorities to access quantum information are presented. Our analysis generalizes the hierarchical structure to more complex ones among more parties in the LOCC setting and provides a stepping stone to understanding hierarchical QIS protocols in a unified manner using graphs for the graph states.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Sec. II, we introduce definitions of the task of extracting quantum information and present the preliminary materials on quantum information extracting tasks, stabilizer codes, and graph states. In Sec. III, we present our main result, Theorem 5 for extracting single-qubit quantum information encoded in a stabilizer code on multiple qubits to a specified qubit by LOCC. In Sec. IV, we provide applications of the protocol for LOCC-QIS obtained in Theorem 5 to Theorem 6. Our conclusion is given in Sec. V.
II settings and Preliminaries
In this section, we define the task of extraction of quantum information and introduce preliminaries. In Sec. II.1 definitions of our task are given. In Sec. II.2 we state useful lemmas of preceding works for the analysis of the task. In Sec. II.3 we summarize a definition of the stabilizer code, by which the quantum information is encoded in our setting; then, we also provide a summary of graph states, which are used in our analysis.
II.1 Settings
We introduce settings and notations about multipartite systems. We consider parties labeled by an integer , and each party has a quantum system represented by a complex Hilbert space. In this paper, denotes the Hilbert space associated with party and the -partite system shared among the parties is represented by the tensor product of , i.e., . Each party only performs local quantum operations on , and classical communication of the outcome of the measurements on between the parties. Quantum operations on the systems held by the other parties and quantum communication between the parties are not allowed. Such a set of quantum operations is called LOCC (local operations and classical communication) [14]. We consider the cases where is a qubit, that is, . single-qubit quantum information encoded in a -qubit system is represented as a quantum state of a two-dimensional subspace of the -qubit Hilbert space. We focus on the cases when is a stabilizer code space specified by a stabilizer , which will be defined in Sec. II.3.
Let be a finite-dimensional Hilbert space, be the set of bounded linear operators on , and be the set of density operators. A quantum state is represented by an element in . A quantum state in a two-dimensional Hilbert space can be represented by using an orthonormal basis called the computational basis as . Let and be the bases of and , respectively. The basis of the code space is called the logical basis. Then extraction of quantum information to party is defined as the task to transform shared over parties to of party by performing a quantum operation over the multipartite system. This quantum operation is represented by a completely positive and trace-preserving (CPTP) map from to [40]. By extraction of quantum information, the quantum information spread over the multipartite system is localized to party , and the quantum information becomes accessible by local operations on .
Our interest is the condition when extraction of quantum information is achievable by LOCC. In the following, a CPTP map that represents LOCC is called an LOCC map. Now, we define the task of extracting quantum information to party by LOCC as follows.
Definition 1 (LOCC extraction of quantum information).
Given a party , let be an isometry map which transforms the logical basis of to the computational basis of . LOCC extraction of quantum information to party is a task represented by an LOCC map which satisfies, for any quantum state ,
| (1) |
We give an example of LOCC extraction of single-qubit quantum information encoded in two qubits in Appendix A.1.
II.2 Preliminaries of extracting tasks
To complete extraction of quantum information, we have to explicitly construct the LOCC map that extracts an arbitrary input state . In this section, we describe how to simplify this construction of the LOCC map based on Ref. [23].
By purification of quantum states [40], any quantum state is represented by a pure state in a composite system represented by , where represents a reference system and . The introduction of the reference system is useful for analyzing extraction of quantum information. The following lemma shows that extraction of quantum information to party is equivalent to a task to transform the maximally entangled state between and to the maximally entangled state between and . Here, the maximally entangled state between and is
| (2) |
and that between and
| (3) |
Due to the following lemma, it suffices to construct a map given by
| (4) |
to seek an LOCC map extracting quantum information to party .
Lemma 1.
We give an example of the state transformation equivalent to the extraction of single-qubit quantum information encoded in two qubits in Appendix A.2.
II.3 Preliminaries for Stabilizer Code and Graph State
We introduce the stabilizer code and the graph state in this subsection. In the following, the Pauli operators and the identity on a qubit are denoted by , and , respectively. Their matrix representations in the basis are,
| (6) |
The Hadamard gate is denoted by , which satisfies and where is defined by .
A stabilizer is defined as an abelian subgroup of a Pauli group, where the Pauli group on qubits is defined as the group generated by Pauli operators on each qubit. For any stabilizer on qubits, there exists an element in which is stabilized by , i.e., for all . If a stabilizer is generated by independent operators, the set of elements stabilized by is a -dimensional linear subspace of and called a stabilizer code. If the stabilizer on qubits is generated by independent generators, the pure state stabilized by is uniquely determined since the subspace stabilized by is one-dimensional. We call this pure state the stabilizer state stabilized by .
The graph state [33] can be used to analyze tasks of extracting quantum information encoded in the stabilizer code. For a given graph , the graph state is defined as follows assuming to be a simple graph. Let be a graph with and qubits be associated with each vertex in . We use the same index to represent the party, the qubit, and the vertex. Graph state is a pure state of qubits represented by
| (7) |
where is the controlled gate on two qubits and acting as
| (8) |
The graph state can also be defined as the unique pure state of fixed by the stabilizer generated by operators
| (9) |
where a superscript of a Pauli operator corresponds to the superscript of the Hilbert space to which each Pauli operator acts, and is the set of vertices adjacent to , i.e., those satisfying . Therefore, a graph state is a stabilizer state. In addition, any stabilizer state can be transformed to a graph state by a local Clifford (LC) operation, which is a local unitary operation transforming a Pauli operator to a Pauli operator [33]. We say two quantum states and of a multiqubit system are LC equivalent if there exists a local Clifford operation which satisfies .
Proposition 2.
LC equivalence between a stabilizer state and a graph state [33]: For any stabilizer state of qubits, there exists a graph state that is LC equivalent to , i.e., for some LC operation . This LC operation and the graph state can be calculated in time.
In LOCC extraction of quantum information, a projective measurement in the eigenbasis of a Pauli operator on a party called a local Pauli measurement (LPM), plays an important role as will be shown in Sec. III. The LPMs on quantum states of an -qubit stabilizer code can be classically simulated in a polynomial time in terms of . This fact is known as the Gottesman-Knill theorem [41, 42]. One could use this property for seeking efficient extraction of quantum information encoded in a stabilizer code, but in this paper, we use the fact that the stabilizer state is LC equivalent to the graph state and that LPMs can be efficiently simulated by representing LPMs as a transformation of the graph such as eliminating vertices and local complementations [33].
The graph obtained by eliminating vertex from graph is represented by , where
| (10) |
The graph obtained by the local complementation on vertex of the graph is represented by , where
| (11) |
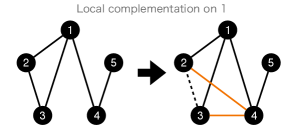
We give a graphical description of the local complementation in Fig. 1.
The LPMs on a graph state are represented as follows. Let and be the eigenstates of and with eigenvalues , respectively, and and be the projection operators to the eigenstates and , respectively. In particular, the measurement in on a qubit of the graph states is simply represented by eliminating the vertex as shown in Fig. 2, and a measurement in on line-topology graph states is represented as shown in Fig. 3.
Proposition 3.
LPM on a graph state, Proposition 7 in Ref. [33] : A measurement in the eigenbasis of on the qubit associated with vertex transforms a graph to a new graph state up to local unitaries . Let be the neighborhood of , and be the local complementation on vertex . The state after a measurement in each basis is given by
| (12) | ||||
| (13) | ||||
| (14) | ||||
where vertex can be any one of the elements of , and the local unitaries are given by
| (15) | ||||
| (16) | ||||
| (17) | ||||
| (18) | ||||
| (19) | ||||
| (20) |
If is an empty set, the obtained state after the measurement is always .


Here, we give a corollary of Proposition 3 about a measurement in on a line-topology graph states, which is illustrated in Fig. 3 and is useful for describing our main result.
Corollary 4.
Measurement in on a qubit of a line-topology graph state: Let be a line-topology graph given by and . A measurement in on maps to , where is the local unitary defined as Proposition 3 and .
III LOCC extraction of stabilizer codes
In this section, we show the necessary and sufficient condition for extracting single-qubit quantum information encoded in a stabilizer code to a fixed party by LOCC. This condition is that the code space of the stabilizer code cannot be expressed as
| (21) |
where is a set of parties including , is the complement of , is a subspace of , and is a state of . In this case, the quantum state of qubit is independent of the encoded quantum information. Therefore, the quantum information is not distributed to party at all. It is interesting to note that quantum information shared among multiple qubits using any stabilizer code can always be extracted to some party by LOCC. This is in contrast to general cases (quantum information shared using a non-stabilizer code), as there are known examples in which extraction is not possible by LOCC in general [22] and may require two-way LOCC [32]. For stabilizer codes, there always exists a party included in , which satisfies the necessary and sufficient condition for LOCC extraction. Thus it is always possible to extract quantum information encoded in the stabilizer code using LOCC to some party.
There are two key elements for the proof of the sufficient and necessary condition. First, as shown in Lemma 1, to prove that arbitrary quantum information can be extracted, we will show that the maximum entangled state of the reference system and code space can be mapped to the maximum entangled state of the reference system and qubit by LOCC without any operations on the reference system. Second, using the fact that the code space is a stabilizer code, we will regard as a graph state up to the LC equivalence; then, the measurement in the eigenbasis of the Pauli operators and the LC operations associated with the outcomes of the measurement can be regarded as a transformation of the corresponding graphs.
Theorem 5.
Let be a given stabilizer on qubits, , generated by independent generators and be a stabilizer code stabilized by . Given a fixed party , there exists an LOCC map which performs extraction of single-qubit quantum information encoded in to party , if and only if there exists no subset which includes such that each state in the logical orthonormal basis of is represented by
| (22) |
where is a set of mutually orthogonal states of , and is a fixed pure state of .
Proof.
Theorem 5 is proved by reducing extraction of quantum information to the problem of considering a graph corresponding to the graph state LC equivalent to and transforming this graph into a connected two-vertex graph representing the reference system and party . The transformation of a graph is composed of (i) eliminating the vertices not included in the path from vertex to vertex , and (ii) the local complementations on the remaining vertices except for vertex and vertex . This graph transformation is implemented by LPMs and LC operations as shown in Algorithm 1. We note that the parties who need to cooperate in Algorithm 1 are only those who are in the path or adjacent to the path; therefore, not all parties need to cooperate on the LOCC extraction of quantum information.
To see how Algorithm 1 works, we give an example of the five-qubit code [3, 4] and graphically explain the process of extraction of quantum information using graphs.
Example 1 (Five-qubit code).
We extract quantum information encoded in the five-qubit code [46], which is known to be able to protect against an arbitrary single-qubit error.
Let us consider the task of extracting quantum information to party according to Algorithm 1. The stabilizer of the five-qubit code is generated by generators
| (23) |
where the tensor product symbol is omitted for brevity.
The graph corresponding to the five-qubit code is given in Fig. 4, which can be calculated according to Appendix B.2. The maximally entangled state between the stabilizer code and the reference is LC equivalent to as
| (24) |
where
| (25) |
Then, the parties perform the sequence of operations to extract quantum information to party 1, according to Algorithm 1. This process is schematically illustrated in Fig. 4, 5, and 6.



We first find a path in the graph from the reference party to a party where information is extracted. We can find the path from vertex 1 to via vertex 2 and vertices 3, 4, and 5 are connected to the path. Since parties in the path and adjacent to the path need to cooperate, all the parties need to cooperate to extract quantum information to party 1 in this case. After parties 4 and 5 perform on their qubits and parties 3, 4, and 5 perform measurements in , suppose that the parties 3, 4, and 5 obtain, e.g., the outcomes , , and , respectively. Then, is transformed to
| (26) |
For these outcomes, the numbers of parties who obtained the outcome and whose vertex is adjacent to party are given by
| (27) |
Therefore, parties 1 and 2 perform gate operation, and the state (26) is transformed to
| (28) |
Next, party 2 performs the measurement in . If the outcome is , the state (28) is transformed to
| (29) |
Since the outcome obtained by party 2 is , party 1 performs the local unitary represented as
| (30) |
and the state (29) is transformed to up to the global phase. This means that the quantum information encoded in the five-qubit code can be extracted to qubit 1 with the above operations.
IV Applications to the quantum information splitting
In this section, we consider applications of Algorithm 1 to the LOCC-QIS, i.e., to share quantum information among multiple parties so that any of the parties cannot extract the shared quantum information on their own but can extract the quantum information only by LOCC. To split and share quantum information is the first step to the quantum secret sharing (QSS) [34, 4, 5], which aims to achieve secure quantum communication if more than a certain number of parties cooperate. The difference between QSS and QIS is that QSS additionally requires that information is kept completely unknown if less than a sufficient number of parties cooperate, while in QIS the information may be partially known. The QIS only requires that the information can be exactly extracted if a sufficient number of parties cooperate. Note that in contrast to the ordinary QIS and QSS settings [34, 4, 5], quantum communication between parties is prohibited in our setting.
In Sec. III, we showed that not every party needs to cooperate to extract quantum information. The number of parties necessary to cooperate depends on to which party the shared quantum information is extracted. In the following, using tree-topology graph states, we propose the LOCC-QIS schemes with a hierarchical structure of authorities to access quantum information shared among multiple parties. The hierarchical structure under the ordinary QIS settings was proposed in Refs. [30, 29, 31] and called hierarchical quantum information splitting (HQIS). Therefore, we call the LOCC-QIS scheme introduced here LOCC-HQIS. We limited ourselves to cases where quantum communication is not possible, but instead, we can design a variety of hierarchical structures corresponding to trees in the graph theory. We will also show that, in a special case, the LOCC-HQIS can be applied to the QSS where the parties can only perform LOCC [19, 20, 21].
IV.1 Notations
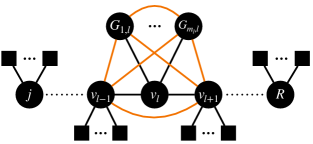
We consider LOCC-HQIS using trees in the following. The set of vertices is divided into and as follows. As shown in Fig. 7, let denote the th subgraph connected to vertex , which has only one vertex adjacent to vertex and is not included in . The path is explicitly represented by
| (31) | ||||
| (32) |
These subgraphs are taken to satisfy the relations given by
| (33) |
| (34) |
where no pair of and has intersection, and denotes the number of vertices adjacent to but not in .

IV.2 A property of protocol for extracting quantum information useful for HQIS
For the stabilizer codes represented by graph states corresponding to trees, Algorithm 1 is optimal for providing the minimal number of parties needed to cooperate. That is, we can identify the hierarchical information access structure of an LOCC-HQIS scheme using such a stabilizer code as presented in the following theorem.
Theorem 6.
Let be a tree of a graph state that is LC equivalent to the maximally entangled state between the reference system and the stabilizer code. The minimum number of parties that need to cooperate for LOCC extraction of quantum information to party equals to
| (35) |
This minimum number of parties is achievable by Algorithm 1; that is, Algorithm 1 is optimal for a tree in terms of the number of parties needed for extracting quantum information.
Proof.
In the proof, we show the following two facts.
-
1.
If any one of the parties corresponding to a vertex in does not cooperate, the extraction of quantum information to party is impossible.
-
2.
If all the parties corresponding to the vertices in one of the subgraphs do not cooperate, the extraction of quantum information to party is impossible.
We show the impossibility of the above two by using the monotonicity of distillable entanglement. If these facts hold, the number of parties needed for the extraction of quantum information must be more than or equal to . Then, Algorithm 1 assures the existence of such an algorithm performed with parties.
See Appendix B.3 for the details. ∎
IV.3 Application of extraction of quantum information using tree states to HQIS
Based on the result shown in the previous subsection, we give four examples of LOCC-HQIS schemes using the stabilizer codes whose corresponding maximally entangled states (Eq. (2)) are given by the tree-topology graph states. First, in Example 2, we consider a scheme using a line-topology graph state as the simplest LOCC-HQIS scheme. Next, in Example 3, we consider a scheme using tree-topology graph states. We also describe that a multiparty HQIS [31] and an -threshold scheme using the Greenberger\UTF2013Horne\UTF2013Zeilinger (GHZ) states [28] in Examples 4 and 5, respectively, are special examples where the hierarchical structures do not change even when the quantum communication is prohibited. Note that in general the hierarchical structure changes depending on whether quantum communication is allowed or not.
In the following example of the line-topology graph with vertices, the party labeled by needs other parties’ cooperation to extract the shared quantum information.
Example 2 (LOCC-HQIS with the line-topology graph with vertices).
Let us consider a graph state on 5 qubits associated with the line-topology graph shown in Fig. 8.

This graph state is also the stabilizer state of the stabilizer generated by the following 5 independent generators
| (36) |
This state can be represented by by regarding it as the maximum entangled state between and the stabilizer code by the stabilizer generated by , and , where its logical operator is .
Now, we consider the extraction of single-qubit quantum information encoded in the stabilizer code of 4 qubits. According to Theorem 6, we can calculate the minimum number of parties needed to cooperate to extract quantum information to . In the case of extracting to party 1, it only needs the cooperation of party 2, regardless of what is performed on parties 3 and 4. Party 2 performs the measurement in and communicates the measurement outcome to party 1, and then 1 performs a local Clifford operation conditioned on the outcome. By contrast, in the case of extracting to party , party needs the cooperation of both party 1 and party 3. Similarly, party needs the cooperation of all the other parties, and party needs it as well. Therefore, this scheme has a hierarchical information access structure. This scheme can be straightforwardly generalized to line-topology graphs with vertices for any .
More complex information access structures can be considered by using trees as shown in the following example.
Example 3 (LOCC-HQIS with the tree with 5 vertices).
Let us consider the tree with 5 vertices shown in Fig. 9.

The multiparty HQIS proposed in Ref. [31] can also be considered as an LOCC-HQIS scheme corresponding to the tree shown in Fig. 10.
Example 4 (The multiparty HQIS among agents).
The tree shown in Fig. 10 corresponds to the multiparty HQIS among agents presented in Ref. [31]. In this scheme, the parties and need only the other parties labeled to extract the quantum information while and need all the other 4 parties under the LOCC setting. Such a hierarchical structure is exactly the same as that shown in Ref. [31] when quantum communication is allowed.

We can also consider the -threshold QSS schemes using GHZ states proposed in Ref. [28] in terms of the graph representation.
Example 5 (The -threshold LOCC-QSS using GHZ states [28]).
The tree shown in Fig. 11 corresponds to the -threshold QSS using the GHZ states [47]. In this scheme, every party needs all the other parties’ cooperation to extract the quantum information. This scheme is relevant to the GHZ states since is represented by
| (37) |
The logical states of this case in the stabilizer code are GHZ states. The state is LC equivalent to the GHZ state on qubits shown in Fig. 11.

From the graph represented in Fig. 11, according to Theorem 6, we can see that all the parties are needed to cooperate for the LOCC extraction of quantum information wherever the information is extracted. The LOCC-QIS scheme corresponding to the GHZ state also works as an -threshold LOCC-QSS scheme, since no information is accessible if one of the parties does not collaborate even when quantum communication is allowed as shown in Ref. [28].
As shown in these examples, our results can serve as a unified theoretical tool for studying the QIS and QSS schemes, especially based on the tree-topology graphs. Using our results in Theorem 6, we can design QIS and QSS schemes with various hierarchical information access structures.
V conclusion
In this paper, we analyzed the task of extracting single-qubit quantum information encoded in the stabilizer code of multiple qubits by introducing parties associated with each qubit. We showed a protocol of LOCC extraction of quantum information to a fixed party given as desired in time in terms of the number of qubits in Theorem 5, whenever possible. The algorithm to find the protocol for extraction of quantum information is given in Algorithm 1. As a consequence of Theorem 5, the quantum information encoded in the stabilizer code can always be extracted to some party by LOCC in time. This algorithm gives an efficient way to decode stabilizer codes, even if we can perform only LOCC rather than multiqubit gates.
Our analysis showed that to extract quantum information, not all parties need to cooperate. The number of parties needed to cooperate depends on which party quantum information is decoded into. Theorem 6 reveals this dependency in cases where the stabilizer code can be represented as a tree-topology graph state up to LC equivalence. Investigating examples, we also showed that this result can be applied to the LOCC-HQIS schemes including the schemes proposed in the past such as the multiparty HQIS [31], which have the hierarchical information access structures among parties in terms of the minimum numbers of parties needed to cooperate. For future works, it is open to investigating the hierarchical structure in the stabilizer codes not corresponding to the tree-topology graphs and characterizing distributed quantum information by these structures.
For future works, it is open to showing if the extraction of more than one-qubit quantum information encoded in the stabilizer code is performed only by LOCC in polynomial time in terms of the number of qubits. Extraction of multi-qubit information is defined as an isometry map which transforms the multi-qubit logical basis to the computational basis of given multiple qubits for extraction. The stabilizer codes with more than one logical qubits have applications to low-overhead fault-tolerant quantum computation [48, 49, 50]. The problem of LOCC extraction of multiple-qubit information from stabilizer codes can be viewed as the problem of extracting multiple Bell states between the reference system consisting of multiple qubits and extraction qubits from a given graph state by LOCC without accessing the reference qubits, similarly to the case of LOCC extraction of single-qubit information.
However, the possibility of extraction of multi-qubit information cannot be determined solely from the connectivity in the graph between the reference vertices (qubits) and the vertices (qubits) where information is extracted unlike the single-qubit case as explained in Appendix C, and therefore, further study is needed to deal with multi-qubit information. The problem to determine the ability to extract multiple Bell states from a given general graph state by LOCC is NP complete. [51]. Nevertheless, there is still a possibility that the problem can be solved efficiently by utilizing the fact that the initial graph state is restricted to the maximum entanglement state between the reference qubits and code space in LOCC extraction, or by imposing an additional restriction to the initial graph state to describe a particular class of stabilizer codes.
For further applications, it would be interesting to investigate the applicability of our LOCC decoding algorithm to implementing faulty non-Clifford measurement used for preparing a magic state encoded in a quantum error-correcting code in fault-tolerant quantum computation (FTQC) [52, 53]. In the faulty non-Clifford measurement, one needs to extract an encoded state of a logical qubit into one of the physical qubits in a similar way to our protocol while the error analysis is also needed for the feasibility of FTQC. Our algorithm may lead to insight into conditions of magic-state-preparation protocols that work for general stabilizer codes.
Acknowledement
KS is supported by Forefront Physics and Mathematics Program to Drive Transformation (FoPM), a World-leading Innovative Graduate Study (WINGS) Program, the University of Tokyo. MM is supported by MEXT Quantum Leap Flagship Program (MEXT QLEAP) JPMXS0118069605, and Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant No. 21H03394. HY acknowledges JST PRESTO Grant Number JPMJPR201A and MEXT Quantum Leap Flagship Program (MEXT QLEAP) JPMXS0118069605, JPMXS0120351339.
Appendix A Examples
A.1 A simple example of extraction of quantum information encoded in two qubits
We consider single-qubit information encoded in a two-qubit system according to the logical basis states of given by
| (38) |
where and are the computational basis states and a tensor product sign for pure states is omitted for brevity. Let be the eigenstates of with the eigenvalues , respectively. To extract quantum information encoded in to of party , party performs a measurement in and communicate the outcome of the measurement to party as shown in the following.
Since can be represented by
| (39) |
the state after the measurement on in with the outcome is given by
| (40) |
and with the outcome is given by
| (41) |
If the outcome is , the state is extracted to party , and if the outcome is , the state can be extracted to party by performing the gate on qubit , where . This protocol only uses LOCC, and thus the protocol implements an LOCC map for extracting quantum information.
A.2 A simple example of a state transformation equivalent to an extraction
According to Lemma 1, LOCC extraction of quantum information in Appendix A.1 is equivalent to the state transformation by LOCC from
| (42) |
to
| (43) |
This transformation can be achieved by the following LOCC protocol. First, party 2 performs a measurement in and communicates the outcome to party 1. Then is transformed to
| (44) |
where the sign of corresponds to the outcome of the measurement. If the outcome is , the state is transformed to . If the outcome of the measurement is , party 1 performs the gate. Then we have . The sequence of operations in this protocol is the same as the one in Appendix A.1.
Appendix B Proofs
B.1 Proof of Theorem 5
We state a useful lemma about quantum state merging [22] to prove Theorem 5. The task in Theorem 5 can be regarded as extracting quantum information to from the bipartite system . The following Lemma 7 gives a necessary condition for LOCC extraction from a bipartite system to .
Lemma 7.
Corollary 6 in Ref. [22]: Consider a tripartite pure state
| (45) |
where and are orthogonal pure states of . If is represented by
| (46) |
where are orthogonal pure states in and is a pure state in , there exists no LOCC map which transforms to .
In the following, after introducing some notations, we will show Algorithm 1 indeed provides an LOCC map which performs extraction of single-qubit quantum information.
Proof of Theorem 5.
As shown in Lemma 1, to construct an LOCC extracting map to party , it suffices to construct an LOCC map which transforms to with its action on the reference system being the identity,
| (47) |
where and are maximally entangled states defined in Eq. (2) and (3). This is a stabilizer state since is a stabilizer state stabilized by the stabilizer generated by , and , where is the logical operator on .
According to Proposition 2, is LC equivalent to some graph state , that is,
| (48) |
where is a local Clifford map on qubit .
Now the problem of LOCC construction of is reduced to the transformation of a graph state to another graph state , which can be considered by using Proposition 3 about LPMs on graph states. The conversion procedure can be summarized as follows (i) -measurements at parties other than the path from to on the graph and correction at parties adjacent to that party except . (ii) -measurements at parties other than and in the path from to and corrections at parties adjacent to that party except for (iii) LC operation on the party to cancel the Clifford operation on the reference, which is intact.
If the vertices and , which correspond to the reference system and party respectively, are not connected by a path on the graph, then does not satisfy the condition in Theorem 5, and LOCC extraction of quantum information is impossible according to Lemma 7. Thus, if party satisfies the condition, and are connected by a path from vertex to vertex . Let denote the vertices of , where , and for each is an edge of . Let be the set of vertices adjacent to some vertex of , which may include itself, i.e.,
| (49) |
where is the set of adjacent vertices to as in Eq. (9).
In Algorithm 1, given a state (48), the parties of perform , and we obtain
| (50) |
where is the unitary acting on the parties corresponding to the parties not included in . Let be the set of the parties of which does not correspond to a vertex of , i.e., . Then, each party of performs measurement in , and communicates the outcome of measurement to the parties to all the vertices of adjacent to vertex except for . Since qubit is a reference qubit, party is just a virtual one and cannot perform any operation. Let denote the number of parties who communicate the outcome to party for each . Then, according to Proposition 3, we obtain
| (51) |
where vertices in the superscripts represent their corresponding parties. Thus, each party except for performs , and we obtain
| (52) |
Next, we consider transforming by the local complementation shown in Fig. 3 in Corollary 4, which corresponds to measurement in and LU operations. Party performs the measurement in . Then, according to Proposition 3, if the outcome is , we obtain
| (53) |
and if the outcome is , we obtain
| (54) |
Therefore, if the outcome is , party and party perform and , respectively. If the outcome is , party performs . Then, we obtain
| (55) |
where
| (56) |
By recursively performing the above operation for , we obtain
| (57) |
where
| (58) |
The case of is exceptional because we cannot perform a local unitary operation on the reference system. Finally, party performs the measurement in , and, according to Proposition 3, we obtain
| (59) | ||||
| (60) | ||||
where is a connected graph with the two vertices and . Thus, by applying an appropriate LU operation on depending on the outcome, we obtain in both cases of the outcomes. ∎
B.2 How to calculate the graph state corresponding to the five-qubit code in Example 1
We show how to calculate the graph state corresponding to the five-qubit code. Let be the stabilizer generated by , and . The logical and are respectively represented by and . Logical and operators on this stabilizer code can be calculated using a standard check matrix as mentioned in Chap. 4 in Ref. [43].
Then, is the stabilizer state, and its stabilizer, , is generated by the following 6 generators
| (61) |
We can transform this set of generators to a (nonunique) canonical one with the transformation as follows [44]. The goal of the transformation is to obtain a set of generators where the Pauli operator acting on the -th qubit of generator is , and the others are or . For this transformation, we can multiply a generator by another generator , and apply the local Clifford operation such as the Hadamard gate .
We first look at the Pauli operators acting on qubit 1 of the generator , which is . In addition, we arbitrarily choose a Pauli operator other than , here, . Then, for the other generators, if the Pauli operator on qubit 1 of the generator is or , we update the generator to , and if the Pauli operator on qubit 1 of the generator is same as the Pauli operator which we chose, then remains same. With the above transformation, the generators are transformed to
| (62) |
Next, we repeatedly perform the above transformation looking at qubit of the generator . Then, the generators are transformed to
| (63) |
We can show from this form of generators that is LC equivalent to the graph state whose graph is given in Fig. 4 as
| (64) |
This is because is stabilized by the stabilizer generated by the following generators, with ,
| (65) |
According to Proposition 2 in Ref. [33], the graph state is the stabilizer state of the stabilizer generated by .
B.3 Proof of Theorem 6
Proof of Theorem 6.
We consider whether a non-cooperative party can block the extraction to party by performing a measurement in a wrong basis, communicating a wrong measurement result, or not communicating the measurement result. As discussed in the main text, we show the following statements.
-
1.
If any one of the parties corresponding to a vertex in does not cooperate, extraction of quantum information to party is impossible.
-
2.
If all the parties corresponding to the vertices in one of the subgraphs do not cooperate, the extraction of quantum information to party is impossible.
To show that LOCC extraction of quantum information is impossible in each case, we consider the reduced state of on the system corresponding to the cooperative parties. We show that the reduced state cannot be transformed to by LOCC using the monotonicity of an entanglement measure under LOCC. Since the reduced state can be considered to be a classical probability mixture of the state after the projective measurement in an orthonormal basis of the system that is traced out, we can use Proposition 3 about LPMs on the graph states.



Let us consider the first case where party does not cooperate. Here, as said above, instead of tracing out , we consider the measurement on since it gives the same reduced state on the composite system of the parties other than . After the measurement in on qubit , if the outcome is , the state of the system is represented by , and if the outcome is , the state is represented by , where
| (66) |
Since the graph corresponding to the state after the measurement in on qubit is represented by Fig. 12 according to Proposition 3, we obtain
| (67) |
where , , and are the graphs in Fig. 12 that are not connected with each other. Thus the state after the measurement in is represented by
| (68) |
where .
In the following, we use the distillable entanglement as an entanglement measure to quantify the bipartite entanglement. The distillable entanglement in the bipartite system consisting of the subsystems and is defined as [13]
| (69) |
where and is the trace norm. Let us consider the system as a bipartite system composed of the system corresponding to and the composite system of two systems corresponding to and respectively. With respect to this bipartition, we obtain since is separable.
According to Lemma 1, if extraction of quantum information is possible, we can transform into by LOCC. Since , and entanglement measure is not increased by LOCC, cannot be transformed into by LOCC. Therefore, extraction of quantum information is impossible without the cooperation of the party corresponding to .
Secondly, we consider the case where none of the parties corresponding to the vertices in a subgraph cooperates. Let us define the orthonormal states of the system consisting of qubits in ,
| (70) | ||||
| (71) |
Since the domain of the reduced state of on the system corresponding to is spanned by the two states given by Eqs. (70) and (71), we can regard the system corresponding to as a qubit. Then, can be regarded as the graph state corresponding to the graph in Fig. 7 by regarding the boxes as vertices.
Without loss of generality, let us consider the case of tracing out the system consisting of . In the same way as in the first case, we consider the measurement in on the qubit corresponding to instead of tracing out the system . The measurement in on the qubit corresponding to can be represented by the transformation of graphs shown in Fig. 13, 14, and 15. The state obtained by the measurement in corresponds to the graph shown in Fig. 15. Then, in the same way as in the first case, the state after the measurement is represented by
| (72) |
where . We can see that is separable and hence . Thus, cannot be transformed into by LOCC. In the same way as the , extraction of quantum information to is impossible if all the parties in do not cooperate, which completes the proof. ∎
Appendix C Two-qubit extraction is not simple
Extending the analysis of LOCC extraction of single-qubit information to that of multi-qubit quantum information is not straightforward since the multi-qubit case involves an additional network untying problem. To exhibit this property, let us consider the following graph shown on the left-hand side in Fig. 16, which represents the maximally entangled state between the two-qubit reference and the stabilizer code with two logical qubits.
Consider extracting information into two qubits, and . As explained in Lemma 1, LOCC extraction to and is equivalent to obtain the maximally entangled state between and , which holds two-ebits of entanglement. In the single-qubit case, we only need to check the connectivity between the reference and the party to be extracted. As , , , and are connected, LOCC extraction seems to be possible from the analysis of only the connectivity of the graph. However, two-qubit information cannot be extracted by LOCC in this case because the graph state is actually not maximally entangled for the bipartition drawn in Fig. 16, since this graph state is LC equivalent to the graph state on the right-hand side in Fig. 16, which can only hold one-ebit of entanglement for this bipartition. As LOCC cannot generate entanglement, we cannot obtain the maximally entangled state between and from the initial graph state.
In general, to determine if LOCC extraction is possible and to give the protocol for LOCC extraction, it is necessary to check all the exponential numbers of graphs that can be transformed by local complementation. Finding a class of stabilizer code with multiple logical qubits for efficient LOCC extraction may be possible, but further investigation should be a future task.

References
- Kimble [2008] H. J. Kimble, The quantum internet, Nature 453, 1023 (2008).
- Wehner et al. [2018] S. Wehner, D. Elkouss, and R. Hanson, Quantum internet: A vision for the road ahead, Science 362, eaam9288 (2018), https://www.science.org/doi/pdf/10.1126/science.aam9288 .
- Cleve et al. [1999] R. Cleve, D. Gottesman, and H.-K. Lo, How to share a quantum secret, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648 (1999).
- Gottesman [2000] D. Gottesman, Theory of quantum secret sharing, Phys. Rev. A 61, 042311 (2000).
- Singh and Srikanth [2005] S. K. Singh and R. Srikanth, Generalized quantum secret sharing, Phys. Rev. A 71, 012328 (2005).
- Noiri et al. [2022] A. Noiri, K. Takeda, T. Nakajima, T. Kobayashi, A. Sammak, G. Scappucci, and S. Tarucha, A shuttling-based two-qubit logic gate for linking distant silicon quantum processors, Nat. Commun. 13 (2022).
- Gottesman and Chuang [1999] D. Gottesman and I. L. Chuang, Demonstrating the viability of universal quantum computation using teleportation and single-qubit operations, Nature 402 (1999).
- Jiang et al. [2007] L. Jiang, J. M. Taylor, A. S. Sørensen, and M. D. Lukin, Distributed quantum computation based on small quantum registers, Phys. Rev. A 76, 062323 (2007).
- Eisert et al. [2000] J. Eisert, K. Jacobs, P. Papadopoulos, and M. B. Plenio, Optimal local implementation of nonlocal quantum gates, Phys. Rev. A 62, 052317 (2000).
- Lemr et al. [2011] K. Lemr, A. Černoch, J. Soubusta, K. Kieling, J. Eisert, and M. Dušek, Experimental implementation of the optimal linear-optical controlled phase gate, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 013602 (2011).
- Chou et al. [2018] K. S. Chou, J. Z. Blumoff, C. S. Wang, P. C. Reinhold, C. J. Axline, Y. Y. Gao, L. Frunzio, M. H. Devoret, L. Jiang, and R. J. Schoelkopf, Teleportation-based realization of an optical quantum two-qubit entangling gate, Nature 561 (2018).
- Peres and Wootters [1991] A. Peres and W. K. Wootters, Optimal detection of quantum information, Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 1119 (1991).
- Horodecki et al. [2009] R. Horodecki, P. Horodecki, M. Horodecki, and K. Horodecki, Quantum entanglement, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 865 (2009).
- Chitambar et al. [2014] E. Chitambar, D. Leung, L. Mančinska, M. Ozols, and A. Winter, Everything you always wanted to know about locc (but were afraid to ask), Commun. Math. Phys. 328, 303 (2014).
- Nielsen [1999] M. A. Nielsen, Conditions for a class of entanglement transformations, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 436 (1999).
- Lo and Popescu [2001] H.-K. Lo and S. Popescu, Concentrating entanglement by local actions: Beyond mean values, Phys. Rev. A 63, 022301 (2001).
- Walgate et al. [2000] J. Walgate, A. J. Short, L. Hardy, and V. Vedral, Local distinguishability of multipartite orthogonal quantum states, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 4972 (2000).
- Bergou [2010] J. A. Bergou, Discrimination of quantum states, J. Mod. Opt. 57, 160 (2010).
- Rahaman and Parker [2015] R. Rahaman and M. G. Parker, Quantum scheme for secret sharing based on local distinguishability, Phys. Rev. A 91, 022330 (2015).
- Wang et al. [2017] J. Wang, L. Li, H. Peng, and Y. Yang, Quantum-secret-sharing scheme based on local distinguishability of orthogonal multiqudit entangled states, Phys. Rev. A 95, 022320 (2017).
- Yang et al. [2015] Y.-H. Yang, F. Gao, X. Wu, S.-J. Qin, H.-J. Zuo, and Q.-Y. Wen, Quantum secret sharing via local operations and classical communication, Sci. Rep. 5, 16967 (2015).
- Yamasaki and Murao [2019a] H. Yamasaki and M. Murao, Quantum state merging for arbitrarily small-dimensional systems, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 65, 3950 (2019a).
- Yamasaki and Murao [2019b] H. Yamasaki and M. Murao, Distributed encoding and decoding of quantum information over networks, Adv. Quantum Technol. 2, 1800066 (2019b).
- Shor [1995] P. W. Shor, Scheme for reducing decoherence in quantum computer memory, Phys. Rev. A 52, R2493 (1995).
- Steane [1996] A. M. Steane, Error correcting codes in quantum theory, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 793 (1996).
- Terhal [2015] B. M. Terhal, Quantum error correction for quantum memories, Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 307 (2015).
- Yamasaki [2019] H. Yamasaki, Entanglement theory in distributed quantum information processing, Ph.D. thesis, The University of Tokyo (2019), arXiv:1903.09655 [quant-ph] .
- Markham and Sanders [2008] D. Markham and B. C. Sanders, Graph states for quantum secret sharing, Phys. Rev. A 78, 042309 (2008).
- Wang et al. [2010a] X.-W. Wang, D.-Y. Zhang, S.-Q. Tang, X.-G. Zhan, and K.-M. You, Hierarchical quantum information splitting with six-photon cluster states, Int. J. Theor. Phys. 49, 2691 (2010a).
- Wang et al. [2010b] X.-W. Wang, L.-X. Xia, Z.-Y. Wang, and D.-Y. Zhang, Hierarchical quantum-information splitting, Opt. Commun. 283, 1196 (2010b).
- Wang et al. [2011] X.-W. Wang, D.-Y. Zhang, S.-Q. Tang, and L.-J. Xie, Multiparty hierarchical quantum-information splitting, J. Phys. B 44, 035505 (2011).
- Yamasaki and Murao [2019c] H. Yamasaki and M. Murao, Spread quantum information in one-shot quantum state merging (2019c), arXiv:1903.03619 [quant-ph] .
- Hein et al. [2006] M. Hein, W. Dür, J. Eisert, R. Raussendorf, M. Van den Nest, and H. Briegel, in Proceedings of the International School of Physics “Enrico Fermi” (IOS press, 2006) arXiv:quant-ph/0602096 .
- Hillery et al. [1999] M. Hillery, V. Bužek, and A. Berthiaume, Quantum secret sharing, Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829 (1999).
- Bandyopadhyay [2000] S. Bandyopadhyay, Teleportation and secret sharing with pure entangled states, Phys. Rev. A 62, 012308 (2000).
- Deng et al. [2005] F.-G. Deng, X.-H. Li, C.-Y. Li, P. Zhou, and H.-Y. Zhou, Multiparty quantum-state sharing of an arbitrary two-particle state with einstein-podolsky-rosen pairs, Phys. Rev. A 72, 044301 (2005).
- Gaertner et al. [2007] S. Gaertner, C. Kurtsiefer, M. Bourennane, and H. Weinfurter, Experimental demonstration of four-party quantum secret sharing, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 020503 (2007).
- Zheng [2006] S.-B. Zheng, Splitting quantum information via w states, Phys. Rev. A 74, 054303 (2006).
- Muralidharan and Panigrahi [2008] S. Muralidharan and P. K. Panigrahi, Quantum-information splitting using multipartite cluster states, Phys. Rev. A 78, 062333 (2008).
- Nielsen and Chuang [2010] M. A. Nielsen and I. L. Chuang, Quantum Computation and Quantum Information: 10th Anniversary Edition (Cambridge University Press, 2010).
- Gottesman [1998] D. Gottesman, The Heisenberg representation of quantum computers, in Group22: proceedings of the XXII International Colloquium on Group Theoretical Methods in Physics, Hobart, July 13-17, 1998 (1998) pp. 32–43, arXiv:quant-ph/9807006 .
- Aaronson and Gottesman [2004] S. Aaronson and D. Gottesman, Improved simulation of stabilizer circuits, Phys. Rev. A 70, 052328 (2004).
- Gottesman [1997] D. Gottesman, Stabilizer Codes and Quantum Error Correction, Ph.D. thesis, California Institute of Technology (1997).
- Van den Nest et al. [2004] M. Van den Nest, J. Dehaene, and B. De Moor, Graphical description of the action of local clifford transformations on graph states, Phys. Rev. A 69, 022316 (2004).
- Moore [1959] E. F. Moore, The shortest path through a maze, in Proc. Int. Symp. Switching Theory, 1959 (1959) pp. 285–292.
- DiVincenzo and Shor [1996] D. P. DiVincenzo and P. W. Shor, Fault-tolerant error correction with efficient quantum codes, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3260 (1996).
- Greenberger et al. [1990] D. M. Greenberger, M. A. Horne, A. Shimony, and A. Zeilinger, Bell’s theorem without inequalities, Am. J. Phys. 58, 1131 (1990).
- Yamasaki and Koashi [2022] H. Yamasaki and M. Koashi, Time-efficient constant-space-overhead fault-tolerant quantum computation (2022).
- Gottesman [2014] D. Gottesman, Fault-tolerant quantum computation with constant overhead, Quantum Info. Comput. 14, 1338–1372 (2014).
- Fawzi et al. [2020] O. Fawzi, A. Grospellier, and A. Leverrier, Constant overhead quantum fault tolerance with quantum expander codes, Commun. ACM 64, 106–114 (2020).
- Dahlberg et al. [2020] A. Dahlberg, J. Helsen, and S. Wehner, Transforming graph states to Bell-pairs is NP-Complete, Quantum 4, 348 (2020).
- Litinski [2019] D. Litinski, Magic State Distillation: Not as Costly as You Think, Quantum 3, 205 (2019).
- Łodyga et al. [2015] J. Łodyga, P. Mazurek, A. Grudka, and M. Horodecki, Simple scheme for encoding and decoding a qubit in unknown state for various topological codes, Sci. Rep. 5, 8975 (2015).