Double reflections Assisted RIS Deployment and Energy-efficient Group Selection in mmWaves D2D Communication
Abstract
Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) offer a viable way to improve the performance of the multi-hop device-to-device (D2D) communication. However, due to the substantial propagation and penetration losses of the millimeter waves (mmWaves), a direct line of sight (LoS) link and close proximity of a device pair are required for a high data rate. Static obstacles like trees and buildings can easily impede the direct LoS connectivity between a device pair. Hence, RIS placement plays a crucial role in establishing an indirect LoS link between them. Therefore, in this work, we propose a set cover-based RIS deployment strategy for both single and double RIS-assisted D2D communication. In particular, we have demonstrated that permitting reflections via two consecutive RISs can greatly lower the RIS density in the environment, preventing resource waste and enabling the service of more obstructed device pairs. After the RIS deployment, for information transfer, we also propose an energy-efficient group selection criteria. Moreover, we prove that sometimes double reflections are more beneficial than single reflection, which is counter-intuitive. Numerical results show that our approach outperforms a random and a recent deployment strategy.
Index Terms:
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs), Millimeter Waves (mmWaves), Device to Device (D2D) Communication, RIS Deployment, Energy-efficiency, Group Selection.I introduction
Due to the exponential increase in the number of users and the demand for a high data rate, there is a heavy crisis in bandwidth [1]. Device-to-device (D2D) [2] communication is one of the prominent solutions for this need. In D2D communication, two proximity users can directly communicate with each other without the help of a base station. Note that we can deliver a high data rate over a limited distance in millimeter waves (mmWaves) D2D communication [3]. However, in mmWaves D2D communication, penetration loss is very high due to the presence of randomly located obstacles and trees [4]. In this context, over the past few decades, technologies called beamforming have been developed to address this need for increased data rates [5]. Regardless of the technical details, the common goal of all of them is to intelligently adapt to the randomly fluctuating wireless channel rather than to control it. Therefore, the so-called reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)[6] is a novel technology that claims to solve this problem. An RIS consists of an array of reconfigurable passive elements embedded in a flat metasurface [7]. Every passive element contains a series of embedded PIN diodes that may be switched between the ON and OFF states by adjusting the biased voltage using a direct current (DC) input line. RISs can change a propagation environment into a desired form [8]. As RIS reflects an incident signal in a desired direction, it does not need any radio frequency chains. The main aim of using RIS is to give an indirect line-of-sight (LoS) path through RIS to blocked device pairs and it also reduces hardware cost [9]. It is noted that an RIS can be used as an amplify and forward (AF) relay, that is, it reflects all signals with an amplification factor [10]. Since RISs consist of many patches, grouping strategies have been proposed by several works [11, 12, 13] to minimize the significant channel estimation overhead in RIS-assisted systems.
I-A Motivation and Contributions
Nowadays RIS-assisted D2D communication forms a new research direction [14, 15, 16], and the majority of recent research focuses on RIS usage by assuming that RISs are already set up and accessible. There are few works of RIS deployment strategy and most of them deployed the RISs considering a single reflection, i.e., for RIS deployment, they considered that a device can communicate with another one via a single RIS. In practice, the secondary reflections are not insignificant, especially in metropolitan settings where the RISs are not widely dispersed [17, 18]. Therefore, in a few cases, double reflections can be impactful when a single reflection are insufficient for RIS-assisted communication. Additionally, by allowing double reflections, we can serve more obstructed device pairs without deploying more RIS. As a result, if we allow two or more consecutive RIS-assisted communications, using less number of RISs, we can get more coverage as well as sum throughput. In this work, we ignored the role of triple and higher order reflections due to significant effective path loss [17]. Here, we employ RISs to create an indirect LoS link between a transmitter and receiver pair in order to establish communication when there is no direct LoS link between them. After deploying the RISs, if a device pair wants to communicate with each other, multiple RIS may be available to assist their communication. Note that a subgroup may provide more energy-efficiency than the entire RIS [19]. Therefore, without using a full RIS, we select a specific energy-efficient subgroup for information transfer among all the available RISs. Our contribution is as follows.
-
•
By dividing the service area into regions, we model the environment by determining which places or regions are obscured from one another’s view by the known obstructions. If a pair of devices lie in two zones such that their LoS link is obstructed then we term them a blind pair. In this typical scenario, our proposed RIS deployment strategy helps to connect these blind pairs by forming an indirect LoS link via reflections from RISs. It identifies the blind pairs, determines candidate locations for RIS deployment and finally selects the exact locations based on a set cover formulation.
-
•
We observe that, it may not be possible to provide an indirect LoS via a single RIS reflections for a few device pairs due to the obstacles’s shape and density. In this case, it is possible to provide an indirect LoS via secondary reflections. Our RIS deployment strategy uses both single and double reflections to cover more blind pairs using less number of RISs.
-
•
Each RIS is divided into a number of non-overlapping subgroups to avoid the channel estimation overhead. After the RISs deployment, we propose an energy-efficient algorithm to find out the appropriate subgroups of an RIS to achieve higher sum throughput.
-
•
We have mathematically proved that in some specific scenarios, double reflections are more energy-efficient than single reflection, which is quite counter-intuitive.
Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed strategy can increase sum throughput significantly and reduce the number of overall RIS deployments in comparison to a random [14] as well as a recent deployment strategy [9].
This paper is organized as follows. In Section II, we have introduced the related and existing works. We have discussed the system model and preliminaries in Section III. The problem formulation is discussed in Section IV. RIS deployment strategy, the group selection strategy, and their analysis are discussed in Section V. Thereafter, in section VI, we have discussed the simulation results and compared this with the existing placement strategies. Finally, in Section VII, we give concluding remarks and the future direction of research.
II Related Work
Numerous recent studies have examined the effects and advantages of RISs in mmWaves D2D communication. The authors in [15] focuses on the uplink of an RIS-assisted D2D-enabled cellular network. Additionally, in [3], the authors discussed the utilization of high-frequency signals like mmWaves to achieve the goal of producing high-speed data rates for short-distance communication. Due to the randomly located obstacles, there is a heavy path loss in mmWaves wireless communication. As a result, if a direct LoS link between a device pair does not exist, we need to bypass the signal. The signals can be bypassed using a single reflection via one RIS or reflections via more than one consecutive RISs. Therefore, RIS-assisted communication is one of the ways to achieve a indirect LoS link between a obstructed device pair [20, 21].
The authors in [9] have provided simulation evidence on how locating RISs near users enhances performance but they have not given any placement strategy for double reflections. In [22], the authors exploit the randomly located obstacles for RIS deployment. But, after RIS deployment, there are still many device pairs that can not communicate with each other and there is a placement strategy in [23] which tries to provide indirect LoS to them using single reflections only. In a single base station and single-user downlink network, the authors of [9] have developed an RIS placement optimization issue to optimize the cell coverage by optimizing the RIS orientation and horizontal distance. A placement strategy using the set cover approach for single RIS-assisted communication has been described in [24]. Note that all the above-mentioned RIS placement strategies are applicable to single RIS-assisted communication. However, the work in [17] shows that the multi-RIS secondary reflections may be used to considerably increase the communication’s range by properly tuning the RISs. In order to increase the data rate, the authors in [15] used the ability of the RISs to change the phase shifts of the elements and provide advantageous beam steering. Assuming that the RISs are already deployed, the authors of [19] have demonstrated that both single- and double-reflected RISs significantly affect multi-hop RIS-assisted communication.
It is clear that RISs are put to innovative use in a variety of ways to improve the caliber of wireless communication services. More specifically, in a D2D communication context, RISs are used to reduce blind pairs, eliminate interferences, and avoid obstacles. However, most of the recent studies assume that the RISs are already deployed randomly [14] or strategically in single-reflected RIS communications [9, 25]. Also in the multi-hop scenario, where secondary reflections are allowed, they assumed that RISs are already deployed. Furthermore, for a large RIS, we have to compute a huge number of channel estimations. As a result, the authors in [13] and [26] discussed a novel RIS grouping strategy to reduce the channel estimation overhead. The study in [17] and [27] examines how RISs can improve energy-efficiency in mmWaves D2D communication. Moreover, wireless communication is greatly impacted by the strategic placement of RISs where double reflections are allowed. Our goal in this work is to strategically position a minimum number of RISs considering both single and double reflections, and select an energy-efficient subgroup to improve network performance.
III System Model and Preliminaries
III-A Network Topology
Consider a wireless communication system that operates in a rectangular area that is partitioned into small squares or grids of unit size which is shown in Fig 1. The rectangular area consists of rows and columns. We assume that each unit square grid is identical with respect to their center and we also assume that the center of the leftmost corner square is the origin. It is noted that the device that will operate in this setting will have highly directed antennas. The position of a user is approximated to the center of the grid within which it lies. We assume that a device can communicate with another device directly if there is a LoS link between them and they are within a threshold distance .
Now, we are presenting a few definitions below which will be used throughout our discussion.
Definition III.1 (Direct LoS link).
If there is no blockage between two users and and they are within a distance then the link between them is called a direct LoS link [22].
Definition III.2 (Blind pair).
A device pair lies within a distance is said to be a blind pair if there is no direct LoS link between them.
Definition III.3 (single reflection).
A device pair is said to be coverable via single reflection if there is no direct LoS link between and but they are connected via an intermediate RIS, i.e., there is a direct LoS link between to an RIS and that RIS to .
Definition III.4 (Double reflections).
The device pair lie within a distance is said to be coverable via double reflections if and can communicate with each other in two-hop using two consecutive RISs and , i.e., there is a direct LoS link between to , to , and to , respectively.
Definition III.5 (Coverable blind pairs).
If a device pair is coverable via single reflection or double reflections or both of them, then it is considered as a coverable blind pair, else it is called a totally blind pair.
III-B User Characteristic
We consider all the devices in this communication scenario to be pseudo-stationary [28], i.e., during communication time, a device does not move outside the grid. We also assume that a device follows any mobility model within a grid at any time instance. However, we presume that a device’s location in a unit grid is roughly determined by the grid’s center. It is noted that if we consider a device is within a grid that means it lies at the center of the grid.

III-C Obstacle Characteristic
Here, we position the obstacle inside the grids following the acquisition of the satellite images. We assume that the satellite images give the proper position of the obstacles. In Fig. 1, we consider that the black cells represent the location of the obstacles. We assume that, if a grid/cell is blocked, it means the whole cell is blocked and there will not be any partially block cells. Multiples of these blocked zones combine to build a polygon that closely resembles the shape and size of the obstruction. Within a blocked cell, a device can not lie, i.e., a device can lie only within the free cells. It is noted that an RIS can not be placed within a blocked cell, it will be strategically placed on poles in the free cells.
III-D RIS Grouping
Obstacles prevent a device pair from directly communicating with one another. Therefore, to provide an indirect LoS between them, we use single and double reflections via one and two consecutive RISs. Let us assume that an RIS consists of rows and columns which are effectively controlled to adjust both the amplitude and phase of the incident waveform. However, only the phase is tuned or optimized, and the amplitude factor is fixed to unity for the purposes of simplicity and mathematical tractability [13]. We use a grouping approach in order to minimize the channel estimation overhead [12]. Furthermore, for a large RIS, the phase shift computation is hard, and a minimum energy is required for each phase shift. Therefore, we divide into number of non-overlapping subgroups to minimize the energy consumption where , and each consists of number of patches, i.e, . It is noted that the number of partitions and the ensuing sub-surfaces are decided upon beforehand [13], and each subgroup is capable of providing a desired throughput. In this scenario, can be in one of two states: ON or OFF. An incident signal’s phase can be altered to a desired direction when an element is in the ON state; when it is in the OFF state, it cannot reflect [13]. Here, we use one particular subgroup instead of using total RIS, and we also assume that a subgroup can serve a single request at a particular instant [29]. Our objective is to select the energy-efficient subgroups for information transfer.
III-E Channel Model
In this communication scenario, let there be number of devices that lie within the free zones. We assume that any two devices and want to communicate with each other and they lie within the free zone and , respectively. Now, depending on the position of the obstacles, and can communicate in three different ways as follows: (i) directly, and can communicate directly if there is no obstacle in between them, i.e., there is a LoS link between them. (ii) via single reflection, and (iii) via double reflections. We suppose that the wireless link experiences both small-scale block fading and large-scale path loss effects. The direct channel from to exhibits small-scale fading and their corresponding path loss factor is , where is the path loss at one meter distance, is the path loss exponent and denote the distance between and .
We also assume that each group of an RIS consists of number of elements. Let and be the channel matrix from to , to and, to , respectively. Note that, unlike the conventional RIS-based approach, the grouping-based approach does not involve a diagonal phase shift matrix of non-zero elements [13]. A common phase shift is applied on the incoming signals, and the product of each point-to-point link determines the total path loss for each of these channel matrices [17]. As a result, the effective channel gain for single and double reflection is given by and , where and are the common phase shift of and , respectively.
III-F Throughput Computation
Here we define a metric, data rate that will be used to quantify the performance of our proposed strategy. Here we assume orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) [30] is used in our communication scenario. Let be the transmitted power, then the signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) at the receiver for single RIS-assisted communication is
| (1) |
and SNR for double RISs reflected communication is
| (2) |
where is the variance of the circularly symmetric zero mean additive white Gaussian noise. Note that, we adjust the common phase shift of (1) and (2) to attain the optimal SNR. Therefore, from Shannon’s capacity formula, we can get the throughput . Hence, by calculating the throughput we can compare the performances.
III-G Energy Efficiency
Here, we define the energy efficiency metric [19], which will be used to measure how well our suggested approach performs. Let be the throughput obtained at the receiver end. Additionally, it requires a total amount of energy for information transfer via a single RIS , where
| (3) |
For two consecutive RIS ( and ) assisted communication the total energy consumption is denoted by where
| (4) |
is the number of packets each with bits, is the transmitted power, and is phase shift power for RIS .
Therefore, energy efficiency for single reflection and double reflections are defined by
| (5) |
respectively. Moreover, we use this metric to select an appropriate subgroup for the information transfer of each blind pair.
IV Problem Formulation
Our objective is to place the minimum number of RISs in strategic locations and for each information transfer, we aim to find an energy-efficient subgroup for abstracted device pair. Therefore, we formulate the problem and break it down into two separate parts: i) RIS deployment and ii) Group selection. Now we are describing these two parts in detail below:
IV-A RIS Deployment
In the first part, we want to formulate an optimization problem to cover a maximum number of blind pairs using the least number of RISs. Note that we do not consider those device pairs that have direct LoS and are totally blind. Let be the set of all coverable blind pairs, i.e., no element of remains uncovered after deploying the RISs. Moreover, to formulate the optimization problem, we define a few notations below.
Let and be two locations and be an indicating variable that describes the status of having LoS between them, where . That is,
| (6) |
Additionally, let be the set of all blind pairs covered by an RIS at the -th cell. That is,
| (7) |
Note that a blind pair of may be visible via a single or double reflections. Therefore, we also consider as a set of all blind pairs that are coverable via double reflections using two RISs located at -th and -th cell but not coverable by either -th or -th RIS via a single reflection. Hence, can be represented as
| (8) |
However, we define as a set of all blind pairs that are coverable via single as well as double reflections using RIS placed at -th and -th locations. That is,
| (9) |
We now introduce the following binary variable:
Hence, we formulate the optimization problem as follows:
| (10) | ||||
| such that | (11) |
This integer program can be linearized by using an intermediate binary variable as follows:
| (12) | ||||
| such that | (13) | |||
| (14) | ||||
| (15) | ||||
| (16) |
Note that the above integer linear program (ILP) is nothing but a classical set cover problem which is a well-known NP-hard problem. Therefore, in Section V-A, we present a greedy solution for the RIS deployment problem.
IV-B Group selection
In the second part, for group selection, we assume that RISs have already been deployed. Moreover, we also know which blind pair will be covered by which RISs. Note that, a blind pair may be covered by single as well as double reflections. Hence, for a blind pair, more than one subgroup may be available to complete the information transfer. However, we allow a single subgroup for information transfer because of the scenario of energy constraints. Therefore, our primary objective is to identify a specific energy-efficient subgroup for each blind pair. Let us assume that there are number of blind pairs, and number of RISs are deployed in the surroundings and each of them is subdivided into number of subgroups. Let be the set of all subgroups that can provide an indirect LoS link to the -th blind pair via single reflection. Hence, we can represent as
Similarly, let be the set of all subgroups that can provide an indirect LoS link to the -th blind pair via double reflections. That is,
Hence, if a blind pair is visible by single reflection, our problem is to find a more energy-efficient subgroup from such that
If a blind pair is visible via double reflections, we select as energy-efficient subgroups from such that
Note that if a blind pair is visible via single as well as double reflections, we will select the more energy-efficient case for them. In Section. V-B, we have discussed the group selection strategy in detail.
V Proposed Strategy
In this section, we discuss the RIS deployment and group selection strategy by considering both single and double reflections. Accordingly, we divide this section into two parts: i) RIS deployment strategy and ii) Group selection criteria. In the first part, we propose a greedy deployment strategy, and in the second part, we investigate an energy-efficient group selection criteria.
V-A Proposed RIS Deployment Strategy
In our proposed RIS deployment strategy, we first identify which blind pairs are present in the surroundings. After identifying the blind pairs, we will find the candidate locations for RIS deployment, and finally select the candidate locations for final deployment. All these steps are now discussed in detail below.
V-A1 Blind Pairs Identification
Let there be number of obstacles and number of device pairs in a region, whose locations are known. We assume that the sides of an obstacle are formed by line segments and is the set of all line segments of obstacles. Additionally, we assume that a device pair can communicate with each other if they reside within distance. Let be the set of all free cells. Algorithm 1 finds whether a device pair is visible via a free cell or not. Here, we aim to find all the blind pairs in a region. To achieve this, we first find the set of all device pairs that may be obstructed by a particular obstacle. Finally, continuing this process for all obstacles, we get the set of all blind pairs, which is described below.
Let be the -th obstacle, be the set of all line segments that constitute , and
| (17) |
denote the set of all vertices of . Therefore, let
be the maximum and minimum -coordinate and -coordinate of the vertices of , respectively. Let
be the set of and coordinates of all the device pairs. Let be the set of device pairs that could potentially be obstructed by . That is,
| (18) |
Let be a set of all blind pairs that could potentially be obstructed by . That is,
| intersect at least | ||||
| (19) |
Continuing this process, for each obstacle, we can compute the set of all blind pairs as follows:
| (20) |
The complete process of blind pair identification is shown in Algorithm 2. Note that our main motivation is to serve a maximum number of blind pairs using indirect LoS via single or double reflections. In this context, we use a novel technique to find out the candidate zones for RIS deployment below.
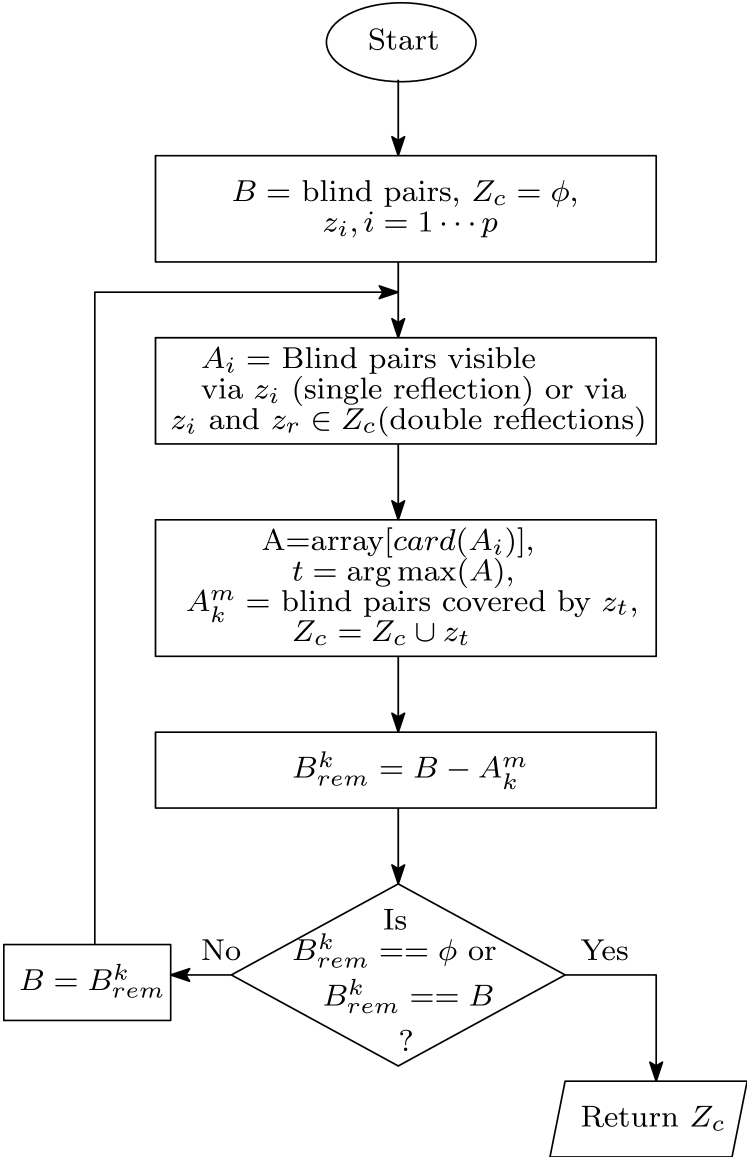
V-A2 Finding Candidate Locations for RIS Deployment
Our goal is to find the candidate locations for RIS deployment such that we can serve a maximum number of blind pairs with fewer RISs. Since the grid consists of rows and columns, there are zones in the grid. Out of zones, few are covered by obstacles, and the remaining are obstacle-free zones. Let there be free zones where and be the set of all free zones. That is,
| (21) |
where denotes the -th free zone.
Let be the set of all blind pairs that are visible via , i.e., for blind pair there is a direct LoS between to and to . Additionally, we denote the cardinality of as . Let be an array of elements whose -th element represents the cardinality of , i.e., . Let be the maximum element of , and be the corresponding index of in the array . Therefore, is the corresponding zone from where the maximum number of blind pairs can be served. Hence, we select as the first candidate location for RIS deployment and be the set of all blind pairs that are visible via . Here we rename the set as and as . Therefore, after finding the initial RIS location, let represent the set of all the remaining blind pairs, i.e.,
| (22) |
where denotes the complement of the set .
After fixing the first candidate location , the remaining blind pairs may be visible via single reflection or double reflections. In particular, the remaining blind pairs in may be visible via single reflection using any free cell other than , or via double reflections using plus one of the remaining free cells. Therefore, we select that free cell as a second candidate location for RIS deployment from where the maximum elements of will be served using single or double reflections. Let us denote as the second candidate zone for RIS deployment, and as the set of remaining blind pairs. In a similar way, we can find out the other candidate locations. Therefore, after finding the -th candidate location, the remaining set of blind pairs is given by
| (23) |
where is the set of all blind pairs that are served by the -th candidate location, and is the set of all remaining blind pairs before finding the -th candidate location and the process will stop if or . Finally, we receive the set of all candidate zones from where we can cover the greatest number of blind pairs. The RISs will actually be placed at the center of each free zone . The proposed strategy is described in Fig. 2.
Complexity of the proposed algorithm
Let there be free cells and many blind pairs. According to our proposed strategy, for selecting the first RIS location, we consider each free cell and compute the number of blind pairs that can be served by it using single reflection only. This requires complexity. Next, for finding the k-th RIS location (), we consider each of the remaining free cells and compute how many blind pairs can be covered by it using single as well as double reflections. This requires complexity. Hence, the worst case complexity of the proposed algorithm is .
From the above discussion and observation, we get the following remarks.
Remark 1.
If and holds then is the total number of uncovered blind pairs. That is, .
Remark 2.
If only number of RISs are allowed to deploy then the total number of blind pairs that can be served is given by .
Remark 3.
In a particular scenario, if no blind pair is visible via double reflections, then our proposed strategy will be converted into the RIS deployment strategy for single reflection.
Below, we have illustrated the proposed RIS deployment strategy using an example.
V-A3 Illustrative Example of the Proposed Deployment Strategy
A specific scenario of our proposed strategy is demonstrated in Fig. 3. Here we consider a grid that consists of four rows and four columns. As this grid consists of sixteen cells, we label these cells from to . Moreover, we assume that the obstacles are located in the black cells, which correspond to the cell numbers , and . We also consider that a device can lie only within a free cell. Here, is the set of all free cells. Here, we assume that each pair of cells is within distance apart from each other. Therefore, in this communication environment,
is the complete set of all the blind pairs. Specifically, there is no direct LoS link between any device pair of . As obstacles block the direct LoS of the blind pairs, RISs can be strategically deployed to provide an indirect LoS link. It can be observed that each of the blind pairs in can not be covered via single reflection, even if we deploy RISs in all the free cells. However, in our proposed strategy, we can serve more blind pairs using double reflections along with the single reflection. It can be observed that maximum number of blind pairs can be served by placing an RIS at cell . Thus, our strategy will choose cell as the first RIS location. Also, note that cells and together can serve all the remaining blind pairs using single and double reflections. That is, according to our proposed strategy, will be the set of locations for RIS deployment.

In Subsection V-B, we will address which subgroup of an RIS will be selected for information transformation.
V-B Group Selection Criteria
In section IV above, we have strategically found , the set of all deployed RISs, and the set of all coverable blind pairs . A blind pair can be covered in three different ways: i) via only single reflection ii) via only double reflections, and iii) via both single and double reflections. Since energy consumption is a very important parameter in wireless communication scenarios, we discuss in the following the process to find the energy-efficient group considering the above-mentioned three cases.
V-B1 Energy-efficient Subgroup Selection for Single Reflection
In this case, sends all the packets to using one subgroup of an RIS as an intermediate reflector. Let be the set of RISs each of which can provide indirect LoS between and via single reflection. That is, u. Since each RIS is partitioned into non-overlapping subgroups, different subgroups may provide different data rates. In this context, from subsection III-G, the required energy for information transfer from to using -th subgroup of -th RIS is given by
| (24) |
where is the phase shift power of -th subgroup of .
Therefore, the energy-efficiency for a particular pair using -th subgroup is
| (25) |
Now, we form an optimization problem to select an energy-efficient subgroup as below:
| (26) | ||||
| s.t. | (27) | |||
| (28) |
where is a predefined threshold.
V-B2 Energy-efficient Subgroup Selection for Double Reflections
In this communication environment, transfers the packets to using two consecutive RISs and , respectively. We also assume that be the set of RISs each of which can provide indirect LoS between and . That is, . Since each RIS is partitioned into non-overlapping subgroups, one subgroup from and another from will be selected for complete information transfer from to . Therefore, from (4), the required energy for complete information transfer using -th and -th subgroup of and respectively, is given by
| (29) |
where, and are the phase shift power for -th and -th subgroup of and , respectively. Moreover, using (5), we compute the energy-efficiency as
| (30) |
Now, we formulate an optimization problem to select the energy-efficient subgroups as follows:
| (31) | ||||
| s.t. | (32) | |||
| (33) |
V-B3 Energy-efficient Subgroup Selection for both Single and Double Reflections
In this communication environment, a device pair is covered by both single and double reflections. That is, and . Therefore, using case V-B1 above, we get a subgroup that provides the maximum energy-efficiency for single reflection. Similarly, using case V-B2 above, we get a pair of subgroups that provide the maximum energy-efficiency for double reflections. Finally, we select the best among them for information transfer between and .
In the following lemmas, we will prove two interesting facts for a device pair covered via both single and double reflections.
Lemma 1.
Let a device pair be visible through using single reflection, and through and together via double reflections. In that case, single reflection are always more beneficial than double reflections.




Proof.
See Appendix A. ∎
From (24) and (29), we observe that energy consumption is a function of data rate, transmit power, and phase shift power. Again, the data rate is a function of distance. Moreover, if a device pair is visible via using single reflection and, and for double reflections where and are three distinct subgroups, the result may be quite different which is counter-intuitive. More specifically, in the following lemma, we prove that double reflections may be more energy-efficient than single reflection depending on the power consumption and the distance traveled by the signal.
Lemma 2.
Let a device pair be visible through using single reflection, and through and together via double reflections, where and are three distinct subgroups. If the following conditions hold:
then double reflections are more energy-efficient than single reflection.
Proof.
See Appendix B. ∎
In the following subsection, we illustrate with an example, the situation where double reflections are more energy-efficient than single reflection.
V-B4 Illustrative Example where Double Reflection is more Beneficial than Single Reflection
In Fig. 4, wants to communicate with and two possible paths are available in between them, one is via using single reflection, and another one via and together using double reflections. Since is located far away from and , the achieved data rate at is not very high. Moreover, due to the close proximity of to , to , and to the achievable data rate at is more than the achievable data rate via the path using which follows from lemma 2. Therefore, in this case, the second path is more energy-efficient. As a result, selects the path via and for complete information transfer using double reflections.
VI Simulation Results
In this section, we conduct comprehensive simulations to verify the effectiveness of our suggested approach and compare it with the closest available methods [9], [14] and [21]. Here we consider a two-dimensional square area of [24]. Furthermore, we assume that two devices can communicate only if they lie within a specific coverage radius. Moreover, we anticipate that D2D communication will occur at a frequency of GHz with a MHz bandwidth [31]. The transmit power is dBm [19] and dBm [32]. Here, we consider a Rician fading scenario [33], incorporating a Rician factor dB [19]. The default parameters taken into account are: path loss at one-meter distance [34], the path loss exponent is and the packet length is bits. Below we briefly describe the existing methods [9], [14] and [21] with which we have compared our proposed approach.
-
•
OPRIS [9]: This work investigates the optimal placement of RISs for a single reflected scenario. In other words, it does not allow double reflections.
-
•
Rand [14]: In this work, the RISs are placed arbitrarily in the geographically separated locations. Here too, the authors investigate the aspect of single reflection.
-
•
DAR [21]: This work proposes an approach to connect a particular device pair by considering the aspect of double reflections. However, it does not include the feature of RIS grouping in the communication scenarios.




Fig. 5(a) shows how many RISs are needed to cover the largest possible region as a function of coverage radius. Here, we consider three different scenarios with three different RIS placement strategies. Consequently, we look at the number of RISs used in these scenarios to get the maximum coverage. Note that, with increasing coverage radius, the number of RISs used exhibits a non-increasing trend, which is quite intuitive. We observe that our strategy outperforms both OPRIS and Rand. This is because, there are many device pairs which are visible via double reflections, but for a single reflection, we need to install a new RIS. As a result, our strategy brings down the requirement of RISs in comparison to OPRIS and Rand, as they did not allow double reflections.
Fig. 5(b) and Fig. 5(c) show how many RISs are needed to cover the largest possible region as a function of device density and number of obstacles, respectively. Accordingly, we look at the number of RISs used in three different scenarios to get the maximum coverage. We find that, for a given situation, the number of RISs increases with the growing density of devices (obstacles), which is quite intuitive. Here too, we observed that our strategy outperforms OPRIS and Rand for the same reason as stated earlier.
Fig. 6(a) shows how the sum throughput and obstacle density are related to each other, where the sum throughput is calculated using equations (1) and (2). Here, we observe that, for a particular scenario, the sum throughput shows a decreasing trend with an increasing number of obstacles. Moreover, our proposed strategy outperforms in comparison to OPRIS and Rand in terms of sum throughput. This is because in our proposed strategy we can serve more blind pairs due to considering the double reflections.
From Fig. 6(b), we observe that, in relation to the growing obstacles, the number of unserved device pairs exhibits a increasing trend. As the number of obstacles increases, the number of blind pairs is also increases. As a result, the likelihood of having more blind pairs that are not served rises. Note that using double reflections, sometimes we can serve some blind pairs that are not possible to serve by single reflection even after deploying more RISs. As a results, our proposed strategy outperforms the performance of OPRIS and Rand in terms of number of unserved blind pairs.
The significance of RIS grouping on the performance metrics, such as achievable throughput and energy efficiency (), as a function of the number of elements in a RIS, is shown in Fig. 7(a). In particular, we examine the effects of distinguishing between a grouping-based scenario (GBS) and a no grouping-based scenario (nGBS). In nGBS, the entire RIS is used for information transfer, whereas in GBS, the RIS is divided into four equal-sized groups and only one of them is used for information transfer. Here, we observe that in both cases, achievable throughput follows an increasing trend with the growing number of elements. This is because a growing number of patches supports better throughput. As a results, nGBS provides higher data throughput as compared to GBS. This makes sense because, in contrast to GBS, nGBS makes use of the entire RIS, whereas GBS only uses a portion of the RIS’s total number of patches. We also observed from 7(a) that, in relation to the rising number of elements in a RIS, the for nGBS is in a decreasing trend whereas it is in an increasing trend for GBS. This is because the required phase shift power in nGBS is proportional to the number of patches of an RIS, whereas a common phase shift power is used for GBS. As a results, usage of the GBS leads to better performance.
In Fig. 7(b), a comparison of energy consumption and energy efficiency between the proposed strategy and the existing benchmark DAR, is shown. Here, as mentioned in 7(a), we partitioned a RIS into four equal parts and selected one of them for communication purposes. Additionally, we consider a scenario, where both strategies use double reflections. In 7(b), we observed that in relation to the growing number of patches of an RIS, exhibits an increasing (decreasing) trend in DAR, and exhibits a decreasing (increasing) trend in our proposed strategy. This improvement is because of the fact that the required phase shift power in DAR is proportional to the number of patches of an RIS as it uses the entire RIS, whereas a particular group is being used and a common phase shift power is used in our proposed strategy.
VII Conclusion
In this work, we proposed a novel RIS deployment strategy in the double RIS-assisted D2D wireless communication scenario, which takes into account the elements grouping of an RIS. The proposed strategy prevents resource wastage by deploying the RIS strategically taking care of both single and double reflections and partitioning the RIS into non-overlapping subgroups. Subsequently, we proposed an energy-efficient group selection strategy for a device pair to complete their communication. It is interesting to note that under some conditions, double reflections are more energy-efficient than single reflection. The simulation results show that a significant reduction in the number of RISs is achievable by allowing double reflections. In addition, double reflections provide more energy efficient communication, and also bring down the number of unserved blind pairs in comparison to some existing benchmarks.
Appendix A Proof of Lemma 1
Let be a blind pair that is visible via using single reflection. Let and be the distances between and , and and , respectively. It is also given that is visible via and together using double reflections, where is a common subgroup that is used in both single and double reflections. Let and be the distances between and , and and , respectively. Additionally, we assume that , and the channel conditions for single and double-reflected communication are the same. Therefore, using triangular inequality, we can claim that
| (34) |
Moreover, from (2), we have
| (from (34) and ) | (35) |
Therefore, from (35), (2) and (1), we can claim that
| (36) |
Now, from (25) and (30), we have
| (37) | |||
| (38) | |||
| (39) |
Therefore, we can conclude from (34) that the transmitted signals from require a longer route for double reflections than for single reflection in order to reach . As a result, due to having a longer path and substantial path loss, the achievable data rate at for double reflections are lower than the single reflection when utilizing a common subgroup. Hence, from (39), we can conclude that if a device pair is coverable by single and double reflections using a common subgroup, single reflection are more beneficial than double reflections which is quite intuitive.
Appendix B Proof of Lemma 2
Here we want to prove that double reflections may be more beneficial than single reflection in some specific scenarios. In this context, for single reflection must be less than for double reflections. Therefore, from (25) and (30), we have
From the stated condition , the required phase shift power for double reflections is always greater than the required phase shift power for single reflection. That is,
| (42) | ||||
| (43) |
Therefore, from (41) and (43), we can claim that
| (44) | |||
Therefore, from (1), (2) and (44), we have
| (45) |
Now, from the stated condition , we can show that
| (46) | |||
| (47) |
Therefore, from (45) and (47), we can claim that
| (48) |
That is, the power gain at the receiver end is greater in double reflections than in single reflection.
Moreover, from (48), we can conclude that if a device pair is visible via single and double reflection and it satisfies the stated conditions, then double reflection is more beneficial than single reflection.
References
- [1] Ericsson Mobility Report, Nov. 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.ericsson.com/en/mobility-report/reports/november-2024.
- [2] R. I. Ansari, C. Chrysostomou, S. A. Hassan, M. Guizani, S. Mumtaz, J. Rodriguez, and J. J. Rodrigues, “5G D2D networks: Techniques, challenges, and future prospects,” IEEE Syst. J., vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 3970–3984, 2017.
- [3] J. Qiao, X. S. Shen, J. W. Mark, Q. Shen, Y. He, and L. Lei, “Enabling device-to-device communications in millimeter-wave 5G cellular networks,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 53, pp. 209–215, Jan. 2015.
- [4] H. Zhao, R. Mayzus, S. Sun, M. Samimi, J. K. Schulz, Y. Azar, K. Wang, G. N. Wong, F. Gutierrez, and T. S. Rappaport, “28 GHz millimeter wave cellular communication measurements for reflection and penetration loss in and around buildings in New York city,” in 2013 IEEE Int. Conf. on Commun., pp. 5163–5167, 2013.
- [5] Q. Xu, C. Jiang, Y. Han, B. Wang, and K. R. Liu, “Waveforming: An overview with beamforming,” IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 132–149, 2017.
- [6] E. Basar, M. Di Renzo, J. De Rosny, M. Debbah, M.-S. Alouini, and R. Zhang, “Wireless communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 116753–116773, Aug. 2019.
- [7] B. Zheng, C. You, and R. Zhang, “Double-IRS assisted multi-user MIMO: Cooperative passive beamforming design,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 20, pp. 4513–4526, July 2021.
- [8] Z. Zhang, Y. Xiao, Z. Ma, M. Xiao, Z. Ding, X. Lei, G. K. Karagiannidis, and P. Fan, “6G wireless networks: Vision, requirements, architecture, and key technologies,” IEEE Veh. Tech. Mag., vol. 14, pp. 28–41, Sep. 2019.
- [9] S. Zengrenzo, H. Zhang, B. Di, Z. Han, and L. Song, “Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) assisted wireless coverage extension: RIS orientation and location optimization,” IEEE Commun. Lett., vol. 25, pp. 269–273, Jan. 2021.
- [10] G. Levin and S. Loyka, “Amplify-and-forward versus decode-and-forward relaying: Which is better?,” in Proc. 22nd Int. Zurich Seminar Commun. (IZS), (Zürich, Switzerland), 2012.
- [11] Z. Li, N. K. Kundu, J. Rao, S. Shen, M. R. McKay, and R. Murch, “Performance analysis of RIS-assisted communications with element grouping and spatial correlation,” IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett., vol. 12, pp. 630–634, Apr. 2023.
- [12] A. Nicolaides, C. Psomas, G. M. Kraidy, S. Yang, and I. Krikidis, “Outage and DMT analysis of partition-based schemes for RIS-aided MIMO fading channels,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 41, pp. 2336 – 2349, Aug. 2023.
- [13] Y. Yang, B. Zheng, S. Zhang, and R. Zhang, “Intelligent reflecting surface meets OFDM: Protocol design and rate maximization,” IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 68, pp. 4522–4535, Jul. 2020.
- [14] S. Jia, X. Yuan, and Y.-C. Liang, “Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in D2D communication network,” IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 683–687, 2020.
- [15] Y. Chen, B. Ai, H. Zhang, Y. Niu, L. Song, Z. Han, and H. Vincent Poor, “Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted device-to-device communications,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 20, pp. 2792–2804, May 2021.
- [16] S. Jia, X. Yuan, and Y.-C. Liang, “Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in D2D communication network,” IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett., vol. 10, pp. 683–687, Mar. 2021.
- [17] T. V. Nguyen, D. N. Nguyen, M. D. Renzo, and R. Zhang, “Leveraging secondary reflections and mitigating interference in multi-IRS/RIS aided wireless networks,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 22, pp. 502–517, Jan. 2023.
- [18] X. Huan, K. S. Kim, S. Lee, E. G. Lim, and A. Marshall, “A beaconless asymmetric energy-efficient time synchronization scheme for resource-constrained multi-hop wireless sensor networks,” IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 68, pp. 1716–1730, Mar. 2020.
- [19] L. Sau, P. Mukherjee, and S. C. Ghosh, “DRAMS: Double-RIS assisted multihop routing scheme for device-to-device communication,” Comput. Commun., vol. 220, pp. 52–63, Apr. 2024.
- [20] J. He, H. Wymeersch, and M. Juntti, “Channel estimation for RIS-aided mmWave MIMO systems via atomic norm minimization,” IEEE Trans.Wireless Commun., vol. 20, no. 9, pp. 5786–5797, 2021.
- [21] Z. Kang, C. You, and R. Zhang, “Double-Active-IRS aided wireless communication: Deployment optimization and capacity scaling,” IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett., vol. 12, pp. 1821–1825, Nov. 2023.
- [22] M. A. Kishk and M.-S. Alouini, “Exploiting randomly located blockages for large-scale deployment of intelligent surfaces,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 39, pp. 1043–1056, Apr. 2020.
- [23] L. Sau and S. C. Ghosh, “A geometry-based strategic placement of RISs in millimeter wave device to device communication,” in Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. Comput. Commun. Engineering. (CCCE), pp. 1–13, Mar. 2023.
- [24] S. Deb and S. C. Ghosh, “An RIS deployment strategy to overcome static obstacles in millimeter wave D2D communication,” in Proc. IEEE 20th Int. Symp. Netw. Comput. Appl. (NCA), pp. 1–8, Nov. 2021.
- [25] X. Mo, L. Gui, K. Ying, X. Sang, and X. Diao, “Reconfigurable intelligent surface deployment for wideband millimeter wave systems,” IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 72, pp. 2989–3004, May. 2024.
- [26] L. Sau, P. Mukherjee, and S. C. Ghosh, “Priority-aware grouping-based multihop routing scheme for RIS-assisted wireless networks,” IEEE Trans. Network Sci. Eng., 2025. early access.
- [27] S. Tewes, M. Heinrichs, R. Kronberger, and A. Sezgin, “IRS-enabled breath tracking with colocated commodity WiFi transceivers,” IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 10, pp. 6870–6886, Apr. 2022.
- [28] D. Singh and S. C. Ghosh, “Mobility-aware relay selection in 5G D2D communication using stochastic model,” IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., vol. 68, no. 3, pp. 2837–2849, 2019.
- [29] M. Jung, W. Saad, M. Debbah, and C. S. Hong, “On the optimality of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs): Passive beamforming, modulation, and resource allocation,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 20, pp. 4347–4363, July 2021.
- [30] T. Weiss, J. Hillenbrand, A. Krohn, and F. Jondral, “Mutual interference in OFDM-based spectrum pooling systems,” in 2004 IEEE 59th Veh. Technol. Conf., vol. 4, pp. 1873–1877, 2004.
- [31] A. Al-Hourani, S. Chandrasekharan, and S. Kandeepan, “Path loss study for millimeter wave device-to-device communications in urban environment,” in 2014 IEEE Int. Conf. on Commun. Workshops (ICC), pp. 102–107, 2014.
- [32] C. Huang, A. Zappone, G. C. Alexandropoulos, M. Debbah, and C. Yuen, “Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 18, pp. 4157–4170, Aug. 2019.
- [33] P. Mukherjee, D. Mishra, and S. De, “Gaussian mixture based context-aware short-term characterization of wireless channels,” IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., vol. 69, pp. 26–40, Jan. 2020.
- [34] Z. Yang, M. Chen, W. Saad, W. Xu, M. Shikh-Bahaei, H. V. Poor, and S. Cui, “Energy-efficient wireless communications with distributed reconfigurable intelligent surfaces,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 21, pp. 665–679, Jan. 2021.