Creating moving gap solitons in spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates
Abstract
A simple and efficient method to create gap solitons is proposed in a spin-orbit-coupled spin-1 Bose-Einstein condensate. We find that a free expansion along the spin-orbit coupling dimension can generate two moving gap solitons, which are identified from a generalized massive Thirring model. The dynamics of gap solitons can be controlled by adjusting spin-orbit coupling parameters.
I Introduction
It is known that the balance between dispersion and nonlinearity may generate solitons [1, 2]. Engineering dispersion and nonlinearity becomes a merited means to control over the existence of solitons and their dynamics. There is a particular kind of engineered dispersion, which is in the form of an avoided energy level crossing with an energy gap that forbids propagation of linear waves. The balance between such dispersion and nonlinearity places solitons inside the energy gap. Due to their specific location, they are named as gap solitons [3, 4]. Generalized massive Thirring models, possessing this dispersion as well as nonlinearity, become an ideal platform to theoretically stimulate gap solitons [5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]. In experiments, periodic potentials can carry out energy gap opening in dispersion. The observation of gap solitons has been implemented experimentally in various nonlinear periodic optical systems, including fiber Bragg gratings [12], waveguide arrays [13], optically induced photonic lattices [14, 15, 16], temporal lattices [17], and microcavities with periodic modulations [18].
In atomic Bose-Einstein condensates (BECs), optical lattices and spin-orbit coupling are responsible for dispersion engineering [19, 20]. Energy gaps can be opened up around Brillouin zone edges by optical lattices. Gap solitons are predicted theoretically [21, 22] and observed experimentally [23] inside these gaps. The study on matter-wave gap solitons in optical lattices soon represents an active research field [1, 2, 24, 25, 26, 27]. Spin-orbit coupling, which can be implemented experimentally by Raman dressing of atomic hyperfine states [28], can modify dispersion in an interesting way that is different from optical lattices. The spin-orbit-coupled dispersion features many degenerated energy minima and has local avoided crossings [29]. It was predicted long time ago that the local spin-orbit-coupled energy gap can mimic generalized massive Thirring model and can support the existence of gap solitonlike solutions [30, 31, 32, 33, 34]. However, until now their experimental observations are not yet achieved.
A possible experimental challenge may lay in preparation. In order to decorate BECs with spin-orbit coupling, Raman lasers are always ramped up adiabatically in experiments [28, 29]. Such loading procedure prepares initial spin-orbit-coupled BECs that are far away from the local energy gaps. It is a challenge for experiments to push initial states into the local energy gaps with high precision. A similar need to transport initial BECs into energy gaps also exists for optical lattices experiments of gap solitons. Precise controllability of optical lattices makes the transport possible. In the experiment, it has been realized by manipulating optical lattices in the way that first accelerating and then keeping optical lattices to move at a constant velocity [23]. In spin-orbit-coupled experiments, it is hard to manipulate Raman lasers. This is because that two pseudo-spin states are coupled resonantly by Raman lasers via a two-photon transition. The adjusting of Raman laser frequency gives rise to an extra time-dependent detuning for the resonant transition. The detuning will destroy effects of spin-orbit coupling.
In the present paper, we propose a simple and efficient approach to create gap solitons in spin-orbit-coupled BECs. This method does not need external operations for pushing initial states. We find that a free expansion triggered by suddenly switching off the harmonic trap along the spin-orbit coupling direction can transfer atoms into the regime of spin-orbit-coupled energy gaps. Atoms inside the regime reach the balance between the dispersion and nonlinearity to form gap solitons.
Our study is in times of rapid advance in the field of spin-orbit-coupled BECs [35, 36, 37, 38]. Various novel phenomena have been revealed theoretically and experimentally in these systems. The study of solitons in spin-orbit-coupled BECs is attracting much attention. Gap solitons in the local energy gaps can exist for both repulsive and attractive interactions [32, 33]. Besides gap solitons, spin-orbit coupling can also support another kind of bright solitons [39, 40]. These solitons are only produced by attractive interactions and exist in the semi-infinite gap of the spin-orbit-coupled dispersion. Various features of these bright solitons have been addressed theoretically [41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48]. It is interesting to mention that spin-orbit coupling can stabilize bright solitons in high dimensions [49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56], which are always unstable without spin-orbit coupling. On the other hand, optical lattices can open global energy gaps in spin-orbit-coupled dispersion [57]. Therefore, spin-orbit-coupled lattices can accommodate gap solitons and the symmetries of spin-orbit coupling bring them new characters [58, 59, 60].
We present a straightforward expansion method to create gap solitons in spin-orbit-coupled spin-1 BECs. The spin-1 spin-orbit coupling has been experimentally implemented in a 87Rb BEC [61]. In the spin-orbit-coupled dispersion, there are two independent local avoided crossings sitting at opposite sides in momentum space. Free expansion can push some atoms into both avoided crossings. Two moving gap solitons can be created and move in opposite direction. The spin-orbit-coupled spin-1 BECs provide versatile and tunable systems to control over dynamics of gap solitons. We adjust spin-orbit-coupled dispersion to slow down one of them and to make one disappear.
The scheme of the paper is organized as follows. In Sec. II, we describe the idea of existence of gap solitons in a spin-orbit-coupled spin-1 BEC. We show the spin-orbit-coupled dispersion has two avoided crossings. An effective model including two bands is built up to analyze dynamics around the avoided crossings. From the effective model, we can get analytical gap soliton solutions. In Sec. III, we demonstrate that free expansion can dynamically generate two moving bright solitons. The solitons are identified to be gap solitons by fitting soliton profiles with analytical gap soliton solutions. In Sec. IV, we describe that dynamics of moving gap solitons can be manipulated, and the conclusion follows in Sec. V.
II Gap solitons in a spin-orbit-coupled spin-1 BEC
Three hyperfine states of 87Rb can be coupled together by three Raman lasers [61]. Along the Raman lasers propagation direction, there are momentum exchanges between lasers and atoms. The proper manipulation of the momentum exchange generates spin-orbit coupling [38]. Such Raman coupling leads to single-particle spin-orbit-coupled Hamiltonian as [61]
| (1) |
with being spin-1 Pauli matrices. The Rabi frequency is proportional to the intensity of Raman lasers. The detuning can be adjusted by changing the frequency of Raman lasers. represents the quadratic Zeeman shift and its value depends on the magnitude of the bias magnetic field. The spin-orbit coupling is denoted by the momentum displacement along the direction (where Raman lasers propagate) for three hyperfine states.
Dynamics of a spin-1 BEC with the Raman-induced spin-orbit coupling is described by the Gross-Pitaevskii equation (GPE),
| (2) |
The wave functions describe occupations of three hyperfine states. The GPE is quasi-one-dimensional, which can be achieved by loading the BEC into an one-dimensional optical dipole waveguide so that motion along the transverse direction are frozen. For the convenience of numerical calculations, the above GPE is dimensionless. The units of length, energy and time are chosen as , and , respectively. Here is the atom mass and is the wavevector with nm the wavelength of Raman lasers [61]. The harmonic trap is with dimensionless relating to the trap frequency , . The interaction coefficient in Eq. (2) is with being the atom number, being the spin-independent scattering length and being the trap frequency along the transverse direction. For a 87Rb BEC, with the Bohr radius. We neglect the spin-dependent scattering length since it is very small in experiments [61]. The wave functions satisfy normalization condition, .
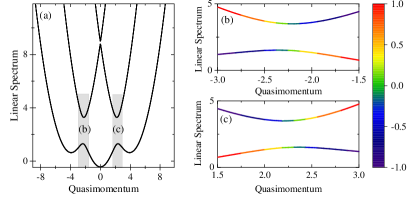
The dispersion relation of the spin-orbit-coupled Hamiltonian has interesting features. A typical dispersion is shown in Fig. 1. In quasimomentum space, there are three parabola locating at and respectively. Local gaps are opened by the Rabi frequency at crossings between parabola. At last, the dispersion relation has three bands. The lowest band possesses three energy local minima. The bias between them can be tuned by changing the detuning and quadratic term. Around the smallest separations between the two lower bands, the dispersion appears as two local avoided energy crossings. In the regimes of avoided crossings [shown by the shadow areas in Fig. 1(a)], the lowest band possesses negative effective mass. The left avoided crossing is dominated by the components and , and the involvement of the component is very small. This is can be seen from the polarization demonstrated by color scales in Fig. 1(b) for the left avoided crossing. While the right avoided crossing is mainly occupied by the components and , and the population of the component can be neglected. The polarization for the right avoided crossing is defined as, , which is demonstrated in Fig. 1(c).
Since the local avoided crossings are far from the higher band and are dominated by two components, if physics is only relevant to the avoided crossings, they can be effectively described by the Hamiltonian,
| (3) |
with eigenstates being two components. and are spin-1/2 Pauli matrices. The dispersion relation of is , having the form of avoided crossing in the quasimomentum space. describes the gap size of the avoided crossing, depicts its steepness, and is the location where the avoided crossing is centered.
The avoided crossings, existing in the spin-orbit-coupled Hamiltonian , provide a versatile bed for the investigation of gap solitons [30, 31, 32]. Assuming atoms are confined around an avoided crossing, their dynamics may be described by the effective model as,
| (4) |
In above equation, interactions between atoms are considered by the last term. The effective model, in literature, is known as a generalized massive Thirring model [5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]. The massive Thirring model, sharing the same but having specific nonlinearity, is completely integrable [62]. The effective model in Eq. (4) includes a generalized nonlinearity. It is known that the outstanding feature of the model is to admit analytical moving gap soliton solutions [7, 8, 30, 31, 32, 63]. They are,
| (5) |
with
| (6) |
| (7) |
and
| (8) |
Two parameters () and () determine the velocity and amplitude of gap solitons.
These moving gap solitons are supported by the avoided crossing dispersion. For the spin-orbit-coupled spin-1 system, two avoided crossings sit at opposite sides with and are far from [as shown in Fig. 1(a)]. In experiments, to artificially introduce spin-orbit coupling into the BEC, Raman lasers should be ramped up adiabatically, in this way, the BEC is always prepared in spin-orbit-coupled ground state which locates at the global minimum of lowest band in the dispersion relation of (i.e., ). In order to create moving gap solitons, the transport of initially prepared BEC from to is prerequisite. However, the precise manipulation of the transport in experiments may be a challenge. In the following, we reveal that a free expansion could be an experimentally accessible way to create moving gap solitons.
III Creating moving gap solitons by expansion
We start from a spin-orbit-coupled ground state obtained by numerically solving Eq. (2) using the imaginary time evolution. The harmonic trap is then suddenly switched off. The quench allows the BEC to expand along the longitudinal direction in the presence of spin-orbit coupling. The interactions between atoms are converted into driving forces to move atoms. If quench-induced excitations are weak comparing with the band separation between the two lower bands in the dispersion relation, the expansion mainly involves the lowest band [20].
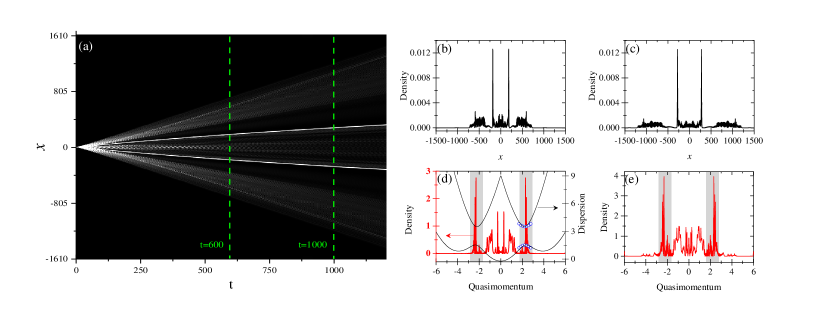
The expansion of total density, , is presented in Fig. 2(a). In coordinate space, the expansion of the total density is symmetric with respect to . Around , two sharp symmetric density peaks appear. They move oppositely at a constant velocity for a very long time and keep their height unchanged. Fig. 2(b) and 2(c) demonstrate two snapshots of the evolution, which are taken at and respectively. Beside the density peaks, there are other excited modes. As the other modes propagate, the density peaks become more obvious. The chosen parameters result in a symmetric dispersion relation with respect to [shown in Fig. 2(d)]. Initial state is centered around . During expansion, quasimomentum is symmetrically extended in opposite directions. As quasimomentum increases, some atoms enter into negative effective mass regimes of lowest band [indicated by shadowed areas in Fig. 2(d) and 2(e)]. When atom number inside these regimes is apparently larger than other occupation of quasimomentum, the density peaks are emergent in coordinate space. Fig. 2(d) and 2(e) show two snapshots of normalized quasimomentum-space density distributions. The normalized quasimomentum-space density is defined as,
| (9) |
with being the density of th component in quasimomentum space. From these plots, it is clear that the occupation of negative effective mass regimes completely dominates. The appearance of the sharp density peaks in coordinate space always accompanies the dominant occupation of negative effective mass regimes. It looks like that some atoms are “trapped” by negative effective mass regimes. Such trapped states can sustain for a long time, this requires a proper range of interaction coefficient: if the coefficient is small, there will be not enough driving resource for expansion to push atoms into negative effective mass regimes; if it is large, atoms in negative effective mass regimes shall be continuously moved out by further expansion.
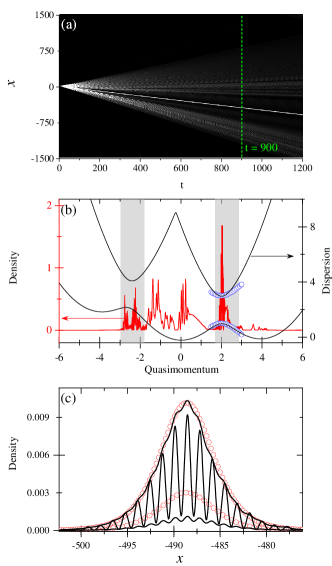
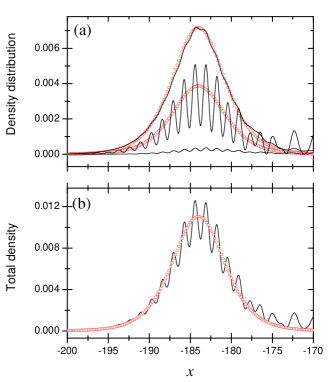
The longevous sharp density peaks in coordinate space in Fig. 2(a) are identified as moving gap solitons. Nearby the negative effective mass regimes, the two lower bands are close to each other and form avoided crossings. The effective model in Eq. (4) provides a simple way to describe atoms inside the regimes. To precisely mimic the avoided crossings in the dispersion of , we first fix the parameters and in by fitting the dispersion of to the avoided crossings. The fitting of the right avoided crossing as an example is demonstrated in Fig. 2(d). We shall reveal that the sharp density peaks are moving gap solitons in Eq. (5). For this purpose, we extract information of the velocity and amplitude of the density peaks. Then we apply them to the analytical gap soliton solutions to fix the free parameters and in Eq. (5). In Fig. 3, we show the negative-direction moving density peak together with the profiles of gap solitons. The density peak is taken at in Fig. 2(a). On account of the mismatch of time origin for the density peak and gap solitons, we choose a that is different from for gap solitons. With this , the center of gap soliton coincides with the density peak. It is shown that profiles of gap solitons match with the density peak very well. Therefore, the density peak is a gap soliton and originates from the occupation of the right avoided crossing. As the right avoided crossing mainly comes from the coupling between and , the occupation of the first component [the bottom solid line in Fig. 3(a)] is very small. We notice that spatial modulation exists in the density peak, which is more evident in the second component [the middle solid line in Fig. 3(a)] . This is because beside the dominant occupation of avoided crossing regimes the expansion also produces some modes around [see Fig. 2(d) and 2(e)]. These modes are primarily composed of the second component , and are occupied by just a few atoms. The interference between them and the density peaks contributes to the modulation on the top of the density peaks. The total density also shows modulation, and gap soliton solution can fit it very well, which is demonstrated in Fig. 3(b).
We conclude that the density peaks are moving gap solitons, which can be created through a free expansion. An initial spin-orbit-coupled BEC can be pushed to occupy the regime of avoided crossings in dispersion relation, where atoms form gap solitons.
IV Manipulating moving gap solitons
In this section, we demonstrate that the spin-orbit-coupled spin-1 system is very versatile for controlling dynamics of gap solitons. It can be achieved by adjusting the detuning in . In the previous section, two symmetric gap solitons can be created with a zero detuning . We reveal that in the presence of the detuning two gap solitons become asymmetric: for a small detuning, two gap solitons have different velocity; for a large detuning one of them disappears.
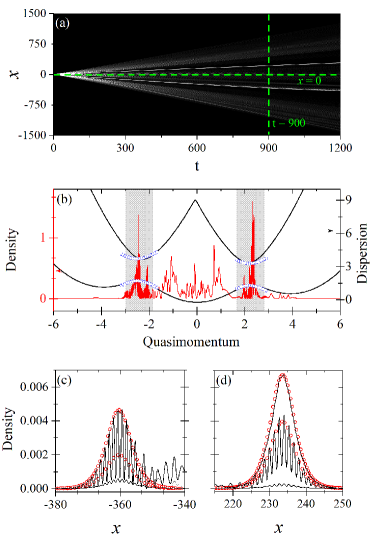
Expansion of the total density with is presented in Fig. 4(a). The expansion can still generate two moving gap solitons. However, the negative-direction moving one has a larger velocity. In the presence of the detuning, the dispersion relation of becomes asymmetric with respect to . The right avoided crossing is energetically lower than the left one, and during the increase of quasimomentum in the expansion more atoms are sent into the right regime as shown in Fig. 4(b). In Fig. 4(c) and 4(d), we match expansion results with analytical gap soliton solutions in Eq. (5). The good match in Fig. 4(c) and 4(d) verifies that the expansion with a small detuning induces asymmetric gap solitons. Oscillations in still exist due to the excited modes around .
Expansion of the total density with a larger detuning () is shown in Fig. 5(a). There is only one soliton produced from background and it moves in the negative direction. With this detuning, the right avoided crossing in the dispersion relation of becomes more obviously lower than the left one [see Fig. 5(b)]. The expansion can easily delivers atoms into the right regime. This causes that there are no enough atoms in the left regime to form gap solitons. Therefore, only atoms in the right regime can form soliton. The density of soliton in Fig. 5(c) shows that populations of and dominate, which confirms that the soliton comes from the occupation of the right avoided crossing. The match presented in Fig. 5(c) proves that the soliton is a gap soliton. It should be noted that the interaction coefficient is smaller than that in Fig. 4. We numerically find that to excite only one soliton the range of would be , which corresponds to the total atom number if the typical transverse tap Hz is considered.
V Conclusion
We present the straightforward free expansion method to create gap solitons in an experimentally realizable spin-orbit-coupled spin-1 BEC. Via expansion, some atoms can be delivered into the regime of spin-orbit-coupled energy gaps to form gap solitons. With this method, the created gap solitons are movable. The idea of our study can be applied to a spin-orbit-coupled spin-1/2 BEC, where only one moving gap solitons is expected to be created.
Acknowledgements.
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China with Grants Nos. 11974235 and 11774219.References
- [1] Y. V. Kartashov, B. A. Malomed, and L. Torner, Solitons in nonlinear lattices, Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 247 (2011).
- [2] V. V. Konotop, J. Yang, and D. A. Zezyulin, Nonlinear waves in PT-symmetric systems, Rev. Mod. Phys. 88, 035002 (2016).
- [3] W. Chen and D. L. Mills, Gap solitons and the nonlinear optical response of superlattices, Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 160 (1987).
- [4] D. L. Mills and S. E. Trullinger, Gap solitons in nonlinear periodic structures, Phys. Rev. B 36, 947 (1987).
- [5] S.-J. Chang, S. D. Ellis, and B. W. Lee, Chiral confinement: an exact solution of the massive Thirring model, Phys. Rev. D 11, 3572 (1975).
- [6] S. Y. Lee, T. K. Kuo, and A. Gavrielides, Exact localized solutions of two-dimensional field theories of massive fermions with Fermi interactions, Phys. Rev. D 12, 2249 (1975).
- [7] D. N. Christodoulides and R. I. Joseph, Slow Bragg solitons in nonlinear periodic structures, Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 1746 (1989).
- [8] A. B. Aceves and S. Wabnitz, Self-induced transparency solitons in nonlinear refractive periodic media, Phys. Lett. A 141, 37 (1989).
- [9] A. R. Champneys, B. A. Malomed, and M. J. Friedman, Thirring solitons in the presence of dispersion, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4169 (1998).
- [10] A. D. Rossi, C. Conti, and S. Trillo, Stability, multistability, and wobbling of optical gap solitons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 85 (1998).
- [11] D. Mihalache, D. Mazilu, and L. Torner, Stability of walking vector solitons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 4353 (1998).
- [12] B. J. Eggleton, R. E. Slusher, C. M. de Sterke, P. A. Krug, and J. E. Sipe, Bragg grating solitons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 1627 (1996).
- [13] D. Mandelik, R. Morandotti, J. S. Aitchison, and Y. Silberberg, Gap solitons in waveguide arrays, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 093904 (2004).
- [14] D. Neshev, A. A. Sukhorukov, B. Hanna, W. Krolikowski, and Y. S. Kivshar, Controlled generation and steering of spatial gap solitons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 083905 (2004).
- [15] O. Peleg, G. Bartal, B. Freedman, O. Manela, M. Segev, and D. N. Christodoulides, Conical diffraction and gap solitons in honeycomb photonic lattices Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 103901 (2007).
- [16] C. Lou, X. Wang, J. Xu, Z. Chen, and J. Yang, Nonlinear spectrum reshaping and gap-soliton-train trapping in optically induced photonic structures, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 213903 (2007).
- [17] C. Bersch, G. Onishchukov, and U. Peschel, Optical gap solitons and truncated nonlinear Bloch waves in temporal lattices, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 093903 (2012).
- [18] D. Tanese, H. Flayac, D. Solnyshkov, A. Amo, A. Lemaître, E. Galopin, R. Braive, P. Senellart, I. Sagnes, G. Malpuech, and J. Bloch, Polariton condensation in solitonic gap states in a one-dimensional periodic potential Nat. Commun. 4, 1749 (2013).
- [19] B. Eiermann, P. Treutlein, Th. Anker, M. Albiez, M. Taglieber, K.-P. Marzlin, and M. K. Oberthaler, Dispersion management for atomic matter waves, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 060402 (2003).
- [20] M. A. Khamehchi, K. Hossain, M. E. Mossman, Y. Zhang, Th. Busch, M. M. Forbes, and P. Engels, Negative-mass hydrodynamics in a spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensate, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 155301 (2017).
- [21] E. A. Ostrovskaya and Y. S. Kivshar, Matter-wave gap solitons in atomic band-gap structures, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 160407 (2003).
- [22] N. K. Efremidis and D. N. Christodoulides, Lattice solitons in Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. A 67, 063608 (2003).
- [23] B. Eiermann, Th. Anker, M. Albiez, M. Taglieber, P. Treutlein, K.-P. Marzlin, and M. K. Oberthaler, Bright Bose-Einstein gap solitons of atoms with repulsive interaction, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 230401 (2004).
- [24] V. Ahufinger and A. Sanpera, Lattice Solitons in Quasicondensates Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 130403 (2005).
- [25] R.-K. Lee, E. A. Ostrovskaya, Y. S. Kivshar, and Y. Lai, Quantum-noise properties of matter-wave gap solitons, Phys. Rev. A 72, 033607 (2005).
- [26] Y. Zhang and B. Wu, Composition relation between gap solitons and Bloch waves in nonlinear periodic systems, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 093905 (2009).
- [27] Y. Zhang, Z. Liang, and B. Wu, Gap solitons and Bloch waves in nonlinear periodic systems, Phys. Rev. A 80 063815 (2009).
- [28] Y.-J. Lin, K. Jiménez-García, and I. B. Spielman, Spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates, Nature, 471, 83 (2011).
- [29] M. A. Khamehchi, Y. Zhang, C. Hamner, Th. Busch, and P. Engels, Measurement of collective excitations in a spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensate, Phys. Rev. A 90, 063624 (2014).
- [30] G. Lenz, P. Meystre, and E. M. Wright, Nonlinear atom optics, Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 3271 (1993).
- [31] G. Lenz, P. Meystre, and E. M. Wright, Nonlinear atom optics: General formalism and atomic solitons, Phys. Rev. A 50, 1681 (1994).
- [32] O. Zobay, S. Pötting, P. Meystre, and E. M. Wright, Creation of gap solitons in Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. A 59, 643 (1999).
- [33] M. Merkl, A. Jacob, F. E. Zimmer, P. Öhberg, and L. Santos, Chiral confinement in quasirelativistic Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 073603 (2010).
- [34] Y. Li, Y. Liu, Z. Fan, W. Pang, S. Fu, and B. A. Malomed, Two-dimensional dipolar gap solitons in free space with spin-orbit coupling, Phys. Rev. A 95, 063613 (2017).
- [35] V. Galitski and I. B. Spielman, Spin-orbit coupling in quantum gases, Nature (London) 494, 49 (2013).
- [36] N. Goldman, G. Juzeliūnas, P. Öhberg, and I. B. Spielman, Light-induced gauge fields for ultracold atoms, Rep. Prog. Phys. 77, 126401 (2014).
- [37] H. Zhai, Degenerate quantum gases with spin-orbit coupling: a review, Rep. Prog. Phys. 78, 026001 (2015).
- [38] Y. Zhang, M. E. Mossman, T. Busch, P. Engels, and C. Zhang, Properties of spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates, Front. Phys. 11, 118103 (2016).
- [39] V. Achilleos, D. J. Frantzeskakis, P. G. Kevrekidis, and D. E. Pelinovsky, Matter-wave bright solitons in spin-orbit coupled Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 264101 (2013).
- [40] Y. Xu, Y. Zhang, and B. Wu, Bright solitons in spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. A 87, 013614 (2013).
- [41] L. Wen, Q. Sun, Y. Chen, D.-S. Wang, J. Hu, H. Chen, W.-M. Liu, G. Juzeliūnas, B. A. Malomed, and A.-C. Ji, Motion of solitons in one-dimensional spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. A 94, 061602(R) (2016).
- [42] E. Chiquillo, Quasi-one-dimensional spin-orbit- and Rabi-coupled bright dipolar Bose-Einstein-condensate solitons, Phys. Rev. A 97, 013614 (2018).
- [43] F. Kh. Abdullaev, M. Brtka, A. Gammal, and L. Tomio, Solitons and Josephson-type oscillations in Bose-Einstein condensates with spin-orbit coupling and time-varying Raman frequency, Phys. Rev. A 97, 053611 (2018).
- [44] N.-S. Wan, Y.-E Li, and J.-K. Xue, Solitons in spin-orbit-coupled spin-2 spinor Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. E 99, 062220 (2019).
- [45] Y. V. Kartashov and V. V. Konotop, Stable nonlinear modes sustained by gauge fields, Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 054101 (2020).
- [46] L.-C. Zhao, X.-W. Luo, and C. Zhang, Magnetic stripe soliton and localized stripe wave in spin-1 Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. A 101, 023621 (2020).
- [47] J. Sun, Y. Chen, X. Chen, and Y. Zhang, Bright solitons in a spin-tensor-momentum-coupled Bose-Einstein condensate, Phys. Rev. A 101, 053621 (2020).
- [48] Y.-J. Wang, L. Wen, G.-P. Chen, S.-G. Zhang, and X.-F. Zhang, Formation, stability, and dynamics of vector bright solitons in a trapless Bose-Einstein condensate with spin-orbit coupling, New J. Phys. 22, 033006 (2020).
- [49] H. Sakaguchi, B. Li, and B. A. Malomed, Creation of two-dimensional composite solitons in spin-orbit-coupled self-attractive Bose-Einstein condensates in free space, Phys. Rev. E 89, 032920 (2014).
- [50] L. Salasnich, W. B. Cardoso, and B. A. Malomed, Localized modes in quasi-two-dimensional Bose-Einstein condensates with spin-orbit and Rabi couplings, Phys. Rev. A 90, 033629 (2014).
- [51] Y.-C. Zhang, Z.-W. Zhou, B. A. Malomed, and H. Pu, Stable solitons in three dimensional free space without the ground state: self-trapped Bose-Einstein condensates with spin-orbit coupling, Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 253902 (2015).
- [52] Sh. Mardonov, E. Ya. Sherman, J. G. Muga, H.-W. Wang, Y. Ban, and X. Chen, Collapse of spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. A 91, 043604 (2015).
- [53] H. Sakaguchi, E. Ya. Sherman, and B. A. Malomed, Vortex solitons in two-dimensional spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates: Effects of the Rashba-Dresselhaus coupling and Zeeman splitting, Phys. Rev. E 94, 032202 (2016).
- [54] Y. Xu, Y. Zhang, and C. Zhang, Bright solitons in a two-dimensional spin-orbit-coupled dipolar Bose-Einstein condensate, Phys. Rev. A 92, 013633 (2015).
- [55] X. Jiang, Z. Fan, Z. Chen, W. Pang, Y. Li, and B. A. Malomed, Two-dimensional solitons in dipolar Bose-Einstein condensates with spin-orbit coupling, Phys. Rev. A 93, 023633 (2016).
- [56] Y. V. Kartashov and V. V. Konotop, Solitons in Bose-Einstein condensates with helicoidal spin-orbit coupling, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 190401 (2017).
- [57] C. Hamner, Y. Zhang, M. A. Khamehchi, M. J. Davis, and P. Engels, Spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates in a one-dimensional optical lattice, Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 070401 (2015).
- [58] Y. V. Kartashov, V. V. Konotop, and F. Kh. Abdullaev, Gap solitons in a spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensate, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 060402 (2013).
- [59] Y. Zhang, Y. Xu, and Th. Busch, Gap solitons in spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates in optical lattices, Phys. Rev. A 91, 043629 (2015).
- [60] H. Sakaguchi and B. A. Malomed, One- and two-dimensional gap solitons in spin-orbit-coupled systems with Zeeman splitting Phys. Rev. A 97, 013607 (2018).
- [61] D. Campbell, R. Price, A. Putra, A. Valdés-Curiel, D. Trypogeorgos, and I. B. Spielman, Magnetic phases of spin-1 spin-orbit-coupled Bose gases, Nat. Commun. 7, 10897 (2016).
- [62] W. E. Thirring, A soluble relativistic field theory, Ann. Phys. (N.Y.) 3, 91 (1958).
- [63] C. M. de Sterke and J. E. Sipe, Coupled modes and the nonlinear Schrödinger equation, Phys. Rev. A 42, 550 (1990).