Anomalous multifractality in quantum chains with strongly correlated disorder
Abstract
We demonstrate numerically that a robust and unusual multifractal regime can emerge in a one-dimensional quantum chain with maximally correlated disorder, above a threshold disorder strength. This regime is preceded by a mixed and an extended regime at weaker disorder strengths, with the former hosting both extended and multifractal eigenstates. The multifractal states we find are markedly different from conventional multifractal states in their structure, as they reside approximately uniformly over a continuous segment of the chain, and the lengths of these segments scale non-trivially with system size. This anomalous nature also leaves imprints on dynamics. An initially localised wavepacket shows ballistic transport, in contrast to the slow, generally subdiffusive, transport commonly associated with multifractality. However, the timescale over which this ballistic transport persists again scales non-trivially with the system size.
Multifractal wavefunctions in quantum systems, which are neither extended nor localised, are characterised by anomalous statistics of their amplitudes [1]. While the effective volume occupied by such states grows unboundedly with system size, it is a vanishing fraction of the system volume; as such, they are often dubbed non-ergodic extended states. This is reflected in the scaling of the moments of the wavefunction amplitudes with system size. For a wavefunction defined on a discrete graph with sites,
where is the so-called multifractal dimension [1].
In the context of short-ranged disordered systems in finite-dimensions, multifractality is often a feature of critical points, such as Anderson transitions [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12] and quantum Hall plateau transitions [13, 14, 15], which are clearly fine-tuned points in parameter space. Multifractality is also realised, often robustly, in several long-ranged disordered hopping models, and fully connected random-matrix ensembles [16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29]. The presence of long-ranged physics, either emergently via diverging correlation lengths in the former, or explicitly via the structure of the models in the latter, unifies the two contexts. An interesting question thus arises: how can a robust multifractal phase be realised in a quantum system with inherently short-ranged interactions/hoppings? One possible avenue in a manifestly out-of-equilibrium setting is the time-periodic modulation of a quasiperiodic system with a mobility edge or a localisation transition [30, 31].
In this work, we demonstrate an alternative pathway to robust multifractality in an inherently short-ranged system, importantly in a time-independent Hamiltonian setting. The central ingredient is strong (in fact maximal, as clarified below) correlations in the disordered on-site potential of a one-dimensional chain. Interestingly, the origin and resultant structure of the multifractal states in such a system is markedly different from that of conventional multifractal states, which are associated with both rare large peaks and long polynomial tails of wavefunction amplitudes. In contrast, the multifractal states we find in this work reside over continuous segments of length in the chain and crucially, within the segments, the wavefunction intensities are approximately uniform; , and 0 elsewhere. Due to this structure, we refer to the states as tabletop states. The multifractality of the wavefunctions is then encoded in the scaling of these tabletop lengths with system size. The anomalous nature of the multifractal states also has implications for dynamics. Multifractality of eigenstates is often accompanied by slow dynamics [32, 33, 30, 34],111It should be noted that multifractality is not always a prerequisite for slow dynamics [49, 34].. However, in this case, we find ballistic spreading of a initially localised wavepacket, but over timescales that scale non-trivially with the system size.

As a concrete model, we consider a disordered tight-binding Hamiltonian on a chain of length ,
| (1) |
where denotes the disorder strength and the on-site potentials are drawn from a multivariate Gaussian distribution, , with zero mean. The correlations in the potential are encoded in the covariance matrix . We take the correlations in the potential to decay with distance as
| (2) |
The key point here is that the correlation is a function of , which implies that in the thermodynamic limit for all sub-extensive , as . In other words, the potentials of two sites a sub-extensive distance apart are completely slaved to each other in the thermodynamic limit. We refer to this as maximal correlations in the disorder [36, 37]. For specificity we choose , but emphasise that the specific functional form of is immaterial. In the following we set . Note that the limit of is singular, as there the model becomes the conventional D Anderson model with all eigenstates exponentially localised [38, 39].
The form of the correlations, (2), endows the disordered potential with an extensive lengthscale ( in this case), such that the potential fluctuations on sub-extensive scales are heavily suppressed and only those at extensive scales survive for large . This is already suggestive that the eigenstates can be extended over lengthscales which scale non-trivially with , resulting in multifractality. In fact, as demonstrated below, we find three distinct regimes as a function of . For sufficiently strong disorder a robust multifractal phase is found, where the average or typical tabletop lengths scale as with ; whereas for weak disorder we find for all eigenstates, indicating an extended phase. For a range of between these two regimes a mixed phase is found, where for a given energy some realisations host extended states and some multifractal. Establishing these robust multifractal and extended regimes with the intervening mixed regime in a model with maximally correlated disorder is the central result of this work, and is summarised in Fig. 1.
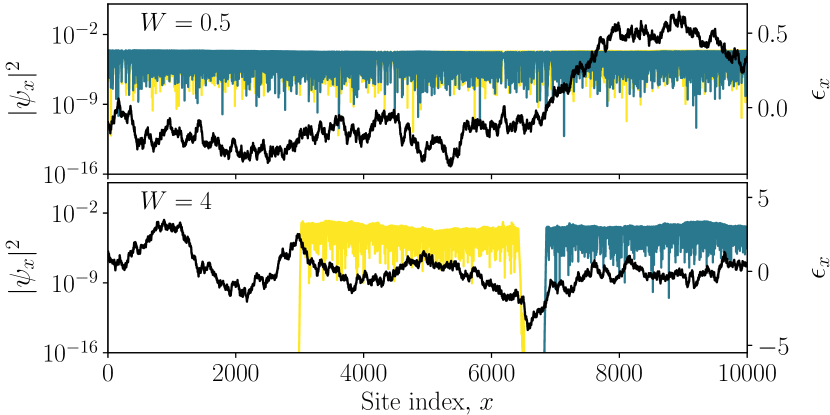
Before delving into a detailed analysis of the statistics of eigenstate tabletop lengths and the consequent multifractality, in Fig. 2 we show explicitly the tabletop nature of eigenstates. Operationally, we extract the tabletop edges for an eigenstate by scanning the chain for sites where the jumps from zero (within numerical precision) and the tabletop length is then simply the distance between the two such sites. It is evident from Fig. 2 that the eigenstates are approximately uniform over the tabletop segments. Hence it is natural to study the distribution of the tabletop lengths , or equivalently of ; denoting these distributions by and respectively. Since we are interested in particular how scales with system size , we define the exponents and from the mean and typical tabletop lengths as
| (3) |
where and similarly for . In addition, we also define the exponent , and study its distribution which we denote by .
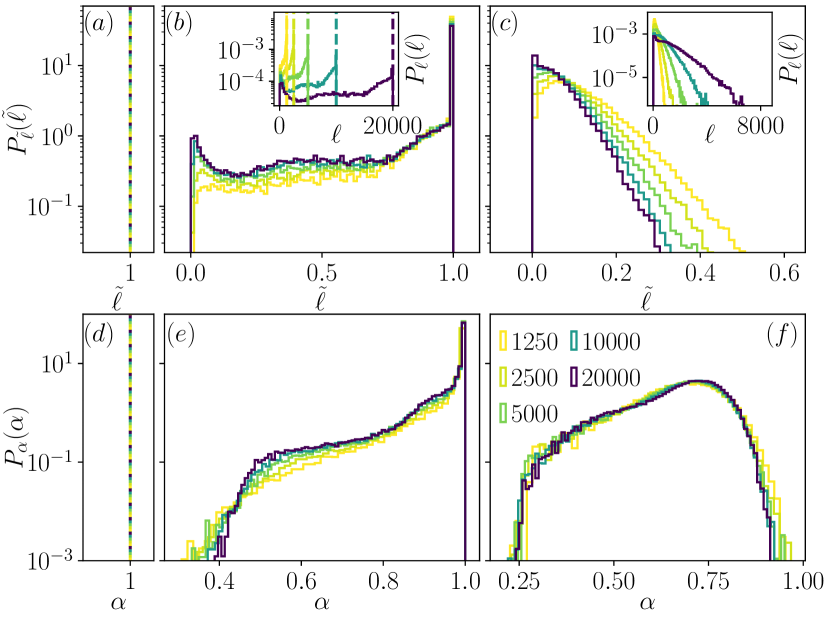
We turn now to numerical results, which unless stated otherwise refer to band centre states (results for other energies remain qualitatively the same). For weak disorder, we find that the tabletops span not only an extensive segment of the chain but the entirety of it, such that or equivalently [Figs. 3(a) and 3(d)]. This is the extended regime indicated in Fig. 1. On increasing , the distribution develops finite weight at sub-extensive while retaining the rest of the weight at extensive [Figs. 3(b) and 3(e)]. This is the mixed regime referred to in Fig. 1. Note that it is important to distinguish the multifractal states with sub-extensive from those that occupy an extensive with , and hence confirm the presence of the former. That this is indeed the case is evidenced in Fig. 3(b) where the weight of the distribution at grows with increasing . Further clear evidence for the mixed regime is also seen in Fig. 3(e) by the fact that retains weight at both and as . Finally, at strong disorder, the system enters a regime where all states in the spectrum are multifractal. As shown in Fig. 3(c), for finite the weight in ultimately decays with increasing , suggesting that there exist no states with extensive tabletop lengths. That all states are indeed multifractal is further confirmed by the distribution (which is well converged with ) having support strictly on as shown in Fig. 3(f). The vanishing of the weight of at and implies respectively the absence of extended and localised states. We add that this three-phase picture is also consistent with results for the scaling of transmittances with , obtained via a transfer matrix calculation [40].
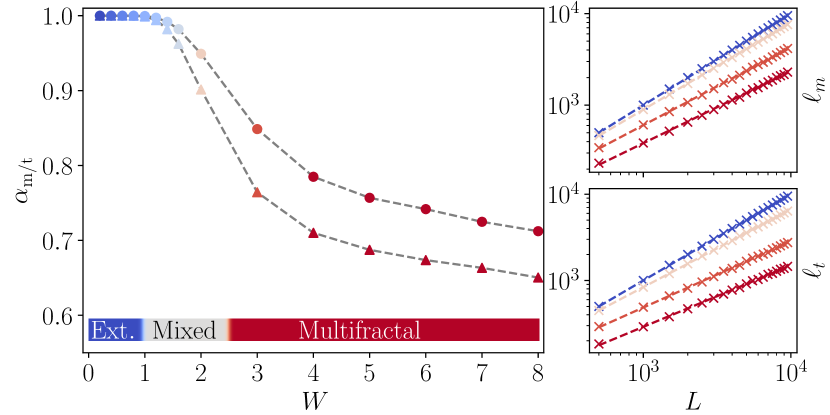
Having established the presence of a multifractal regime, along with an extended and a mixed regime, based on the distributions and , we next present results for the scaling of mean and typical tabletop lengths with . In particular, Fig. 4 shows results for and (defined in Eq. 3) as a function of . For weak disorder we find both and , consistent with the presence solely of extended states. On increasing and entering the mixed regime, and decrease from 1, indicating the emergence of multifractal states in the spectrum. Note that on entering the mixed regime, deviates from 1 less markedly than . This is natural, as in the presence of both extended and multifractal states the mean is dominated by the extended states with , whence is closer to 1 than . Finally, on increasing further into the regime where the spectrum has solely multifractal states, and continue to decrease monotonically.
We close our analysis of the multifractal statistics of tabletop eigenstates with results of a standard probe of multifractality, the generalised inverse participation ratios (IPR), defined as . We will be interested in the scaling with of both the mean and typical IPR,
| (4) |
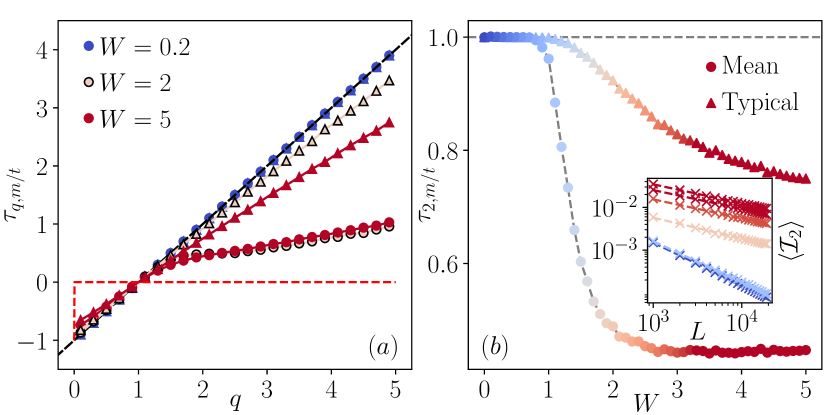
Extended states have , while for exponentially localised states for . An intermediate behaviour for indicates multifractal states [1]. Fig. 5(a) shows results for and , for representative values in each of the three regimes. For the weakest disorder, which lies in the extended regime, we indeed find . The presence of multifractal states upon increasing is borne out by for . In Fig. 5(b), we focus on as a function of . Note that on increasing and entering the mixed regime, deviates from the ergodic value of 1 more markedly than , reflecting the fact that the mean IPR is dominated by the small fraction of multifractal states which have qualitatively larger IPRs than the extended ones.
An explanatory comment is in order regarding the lack of energy resolution between extended and multifractal states in the mixed regime. The density of states (DoS) for the model (1) with the correlated disorder (2) can be shown to fluctuate strongly across disorder realisations [40]. For each realisation we choose to refer energies relative to the centre of the spectrum (tantamount to ). However, the fluctuations in all higher moments of the DoS also remain finite in the thermodynamic limit. As a result, whether an eigenstate at a given energy (relative to the centre of the spectrum) is extended or multifractal depends on the specific disorder realisation (though for any given realisation, multifractal and extended states do not of course coexist at the same energy). Averaging over disorder realisations therefore smears out any energy resolution in the mixed regime, thereby precluding the traditional notion of a mobility edge in the averaged DoS.
So far, we have focussed on ‘static’ properties of the model. Since multifractality often goes hand in hand with slow dynamics [32, 33, 30, 34], it is worth asking what imprint the anomalous multifractal states leave on the dynamics in the present case. In order to answer this question, we consider the spreading of an initially localised wavepacket, in particular its second moment defined as
| (5) |
with . The simplest expected behaviour for is
| (6) |
with crossover scale . For example, would correspond to ballistic transport until the wavepacket spans the entire system; while for localised states , indicating the absence of transport. Conventionally, multifractal states lead to [32, 33, 30, 34].
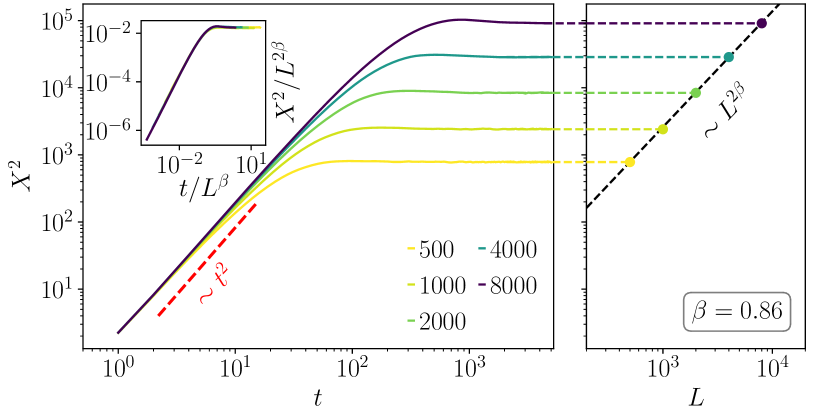
Fig. 6 shows results for the maximally correlated model in the pure multifractal phase. Remarkably, the transport is ballistic with but the saturation of scales as with exponent . In fact, the inset in Fig. 6 shows the scale-collapsed behaviour with for , which confirms the ballistic spreading and sub-extensive saturation of the wavepacket. We now show how a toy model of the anomalous multifractal states qualitatively rationalises the above dynamics.
For simplicity, let us assume that in a given realisation the initially localised wavepacket lies at the centre of a tabletop segment of length . Approximating the eigenstates therein as fully extended over the segment, the wavepacket spreads as a truncated Gaussian
| (7) |
where we have absorbed the velocity into the units of time. for the wavepacket (7) behaves in time as
| (8) |
Averaging over disorder is equivalent to integrating over the probability distribution of the initial site residing in a tabletop of length , denoted by . Thus
| (9) |
For timescales much smaller than a typical tabletop length, the second term in Eq. 9 is negligibly small and the ballistic behaviour is recovered. In the opposite limit where is much larger than typical tabletop lengths (such that in (9)), the wavepacket spreading saturates and , which one expects to scale non-trivially with due to that of .
Finally, we provide a simple heuristic argument for the physics underlying the emergence of the multifractal regime. Note that with the form of the correlations, , the sequence of site energies is readily shown to be a martingale. Thus, given , is a Gaussian random number with mean and variance . This leads to the site energies of nearby sites being very close to each other with high probability; to which we attribute the approximately uniform across the tabletop segment. However, since the conditional distribution is a Gaussian, it has unbounded support. As a result, with very low probability, there can be neighbouring sites where the site energies are wildly different. The break in the tabletops may be attributed to such rare regions. Moreover, as the sequence of site energies is a martingale, the probability of a tabletop terminating at a site is independent of the energies of the sites prior to it. It is then intuitively natural to regard the tabletop breaks as a Poisson process. This in turn implies where is the density of tabletop breaks, which decays with increasing 222As each tabletop state has two breaks, and the density of tabletops of length is .. An exponential with a rate that decays with is indeed consistent with the numerical results shown in Fig. 3(c) in the strong disorder regime. Obviously, however, obtaining the precise multifractal exponents would require a theory which takes into account the fluctuations of within the tabletop length.
In summary, we demonstrated numerically that a one-dimensional quantum chain (1), with maximally correlated disorder (2), hosts a robust multifractal regime. These multifractal eigenstates are strikingly unusual. They reside approximately uniformly over segments of the chain whose lengths scale non-trivially with , whence the multifractal statistics arise. Such an anomalous structure also leaves imprints on the dynamics – in the multifractal phase an initially localised wavepacket spreads ballistically, but over timescales that scale as with , beyond which the expansion saturates.
We note that the behaviour found here differs radically 333Perhaps expectedly, given that the Hausdorff dimension of any tree with is infinite, while that of a 1D chain is unity. from the same model considered on a tree with connectivity [37], which hosts localised states but not a multifractal phase. The present work is also very different from earlier studies [43, 44] of 1D Anderson localisation with long-ranged, power-law (and hence scale-free) disorder correlations. These models too do not host a robust multifractal regime. This suggests that the system-size dependent scale introduced by the correlations (2), along with the martingale nature of the site-energies, is responsible for the robust multifractal regime in the 1D model with maximally correlated disorder.
Finally, it is interesting to note that the effective Fock-space disorder in a many-body localised system is likewise maximally correlated [36], and the many-body localised eigenstates indeed exhibit multifractality on the Fock space [45, 46, 47, 48]. Whether a concrete connection between maximal disorder correlations and multifractality exists, and if so under what conditions, remains an open question.
Acknowledgements.
We thank Ivan Khaymovich for helpful comments on the manuscript. This work was supported in part by EPSRC, under Grant No. EP/L015722/1 for the TMCS Centre for Doctoral Training, and Grant No. EP/S020527/1.References
- Evers and Mirlin [2008] F. Evers and A. D. Mirlin, Anderson transitions, Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 1355 (2008).
- Wegner [1980] F. Wegner, Inverse participation ratio in 2+ dimensions, Z. Phys. B 36, 209 (1980).
- Castellani and Peliti [1986] C. Castellani and L. Peliti, Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General 19, L429 (1986).
- Chalker [1988] J. T. Chalker, Scaling and correlations at a mobility edge in two dimensions, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 21, L119 (1988).
- Chalker [1990] J. T. Chalker, Scaling and eigenfunction correlations near a mobility edge, Physica A 167, 253 (1990).
- Bauer et al. [1990] J. Bauer, T.-M. Chang, and J. L. Skinner, Correlation length and inverse-participation-ratio exponents and multifractal structure for Anderson localization, Phys. Rev. B 42, 8121 (1990).
- Schreiber and Grussbach [1991] M. Schreiber and H. Grussbach, Multifractal wave functions at the Anderson transition, Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 607 (1991).
- Janssen [1994] M. Janssen, Multifractal analysis of broadly-distributed observables at criticality, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 08, 943 (1994).
- Chalker et al. [1996] J. T. Chalker, V. E. Kravtsov, and I. V. Lerner, Spectral rigidity and eigenfunction correlations at the Anderson transition, JETP Letters 64, 386 (1996).
- Mirlin and Evers [2000] A. D. Mirlin and F. Evers, Multifractality and critical fluctuations at the Anderson transition, Phys. Rev. B 62, 7920 (2000).
- Evers and Mirlin [2000] F. Evers and A. D. Mirlin, Fluctuations of the inverse participation ratio at the Anderson transition, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 3690 (2000).
- Cuevas et al. [2001a] E. Cuevas, M. Ortuño, V. Gasparian, and A. Pérez-Garrido, Fluctuations of the correlation dimension at metal-insulator transitions, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 016401 (2001a).
- Chalker and Coddington [1988] J. T. Chalker and P. D. Coddington, Percolation, quantum tunnelling and the integer Hall effect, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 21, 2665 (1988).
- Huckestein [1995] B. Huckestein, Scaling theory of the integer quantum Hall effect, Rev. Mod. Phys. 67, 357 (1995).
- Evers et al. [2001] F. Evers, A. Mildenberger, and A. D. Mirlin, Multifractality of wave functions at the quantum Hall transition revisited, Phys. Rev. B 64, 241303 (2001).
- Levitov [1990] L. S. Levitov, Delocalization of vibrational modes caused by electric dipole interaction, Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 547 (1990).
- Mirlin et al. [1996] A. D. Mirlin, Y. V. Fyodorov, F.-M. Dittes, J. Quezada, and T. H. Seligman, Transition from localized to extended eigenstates in the ensemble of power-law random banded matrices, Phys. Rev. E 54, 3221 (1996).
- Parshin and Schober [1998] D. A. Parshin and H. R. Schober, Multifractal structure of eigenstates in the Anderson model with long-range off-diagonal disorder, Phys. Rev. B 57, 10232 (1998).
- Levitov [1999] L. S. Levitov, Critical Hamiltonians with long range hopping, Annalen der Physik 8, 697 (1999).
- Varga and Braun [2000] I. Varga and D. Braun, Critical statistics in a power-law random-banded matrix ensemble, Phys. Rev. B 61, R11859 (2000).
- Cuevas et al. [2001b] E. Cuevas, V. Gasparian, and M. Ortuño, Anomalously large critical regions in power-law random matrix ensembles, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 056601 (2001b).
- Cuevas [2003] E. Cuevas, Multifractality of Hamiltonians with power-law transfer terms, Phys. Rev. B 68, 184206 (2003).
- Monthus and Garel [2010] C. Monthus and T. Garel, The Anderson localization transition with long-ranged hoppings: analysis of the strong multifractality regime in terms of weighted Lévy sums, J. Stat. Mech. , P09015 (2010).
- Kravtsov et al. [2015] V. E. Kravtsov, I. M. Khaymovich, E. Cuevas, and M. Amini, A random matrix model with localization and ergodic transitions, New Journal of Physics 17, 122002 (2015).
- Deng et al. [2019] X. Deng, S. Ray, S. Sinha, G. V. Shlyapnikov, and L. Santos, One-dimensional quasicrystals with power-law hopping, Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 025301 (2019).
- Monthus [2019] C. Monthus, Multifractality in the generalized Aubry–André quasiperiodic localization model with power-law hoppings or power-law Fourier coefficients, Fractals 27, 1950007 (2019).
- Khaymovich et al. [2020] I. M. Khaymovich, V. E. Kravtsov, B. L. Altshuler, and L. B. Ioffe, Fragile extended phases in the log-normal Rosenzweig-Porter model, Phys. Rev. Research 2, 043346 (2020).
- Kravtsov et al. [2020] V. E. Kravtsov, I. M. Khaymovich, B. L. Altshuler, and L. B. Ioffe, Localization transition on the random regular graph as an unstable tricritical point in a log-normal rosenzweig-porter random matrix ensemble (2020), arXiv:2002.02979 [cond-mat.dis-nn] .
- Biroli and Tarzia [2021] G. Biroli and M. Tarzia, Lévy-Rosenzweig-Porter random matrix ensemble, Phys. Rev. B 103, 104205 (2021).
- Roy et al. [2018] S. Roy, I. M. Khaymovich, A. Das, and R. Moessner, Multifractality without fine-tuning in a Floquet quasiperiodic chain, SciPost Phys. 4, 25 (2018).
- Sarkar et al. [2021] M. Sarkar, R. Ghosh, A. Sen, and K. Sengupta, Mobility edge and multifractality in a periodically driven Aubry-André model, Phys. Rev. B 103, 184309 (2021).
- De Tomasi et al. [2016] G. De Tomasi, S. Roy, and S. Bera, Generalized Dyson model: Nature of the zero mode and its implication in dynamics, Phys. Rev. B 94, 144202 (2016).
- Monthus [2017] C. Monthus, Multifractality of eigenstates in the delocalized non-ergodic phase of some random matrix models: Wigner–Weisskopf approach, J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 50, 295101 (2017).
- Khaymovich and Kravtsov [2021] I. M. Khaymovich and V. E. Kravtsov, Dynamical phases in a “multifractal” Rosenzweig-Porter model, SciPost Phys. 11, 45 (2021).
- Note [1] It should be noted that multifractality is not always a prerequisite for slow dynamics [49, 34].
- Roy and Logan [2020a] S. Roy and D. E. Logan, Fock-space correlations and the origins of many-body localization, Phys. Rev. B 101, 134202 (2020a).
- Roy and Logan [2020b] S. Roy and D. E. Logan, Localization on certain graphs with strongly correlated disorder, Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 250402 (2020b).
- Anderson [1958] P. W. Anderson, Absence of diffusion in certain random lattices, Phys. Rev. 109, 1492 (1958).
- Mott and Twose [1961] N. F. Mott and W. D. Twose, The theory of impurity conduction, Advances in Physics 10, 107 (1961).
- [40] See supplementary material at [URL] for (I) results on transmittance and (II) derivation of the lack of self-averaging in the density of states.
- Note [2] As each tabletop state has two breaks, and the density of tabletops of length is .
- Note [3] Perhaps expectedly, given that the Hausdorff dimension of any tree with is infinite, while that of a 1D chain is unity.
- Izrailev and Krokhin [1999] F. M. Izrailev and A. A. Krokhin, Localization and the mobility edge in one-dimensional potentials with correlated disorder, Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 4062 (1999).
- Croy et al. [2011] A. Croy, P. Cain, and M. Schreiber, Anderson localization in 1d systems with correlated disorder, Eur. Phys. J. B 82, 107 (2011).
- De Luca and Scardicchio [2013] A. De Luca and A. Scardicchio, Ergodicity breaking in a model showing many-body localization, Europhys. Lett. 101, 37003 (2013).
- Macé et al. [2019] N. Macé, F. Alet, and N. Laflorencie, Multifractal scalings across the many-body localization transition, Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 180601 (2019).
- De Tomasi et al. [2021] G. De Tomasi, I. M. Khaymovich, F. Pollmann, and S. Warzel, Rare thermal bubbles at the many-body localization transition from the Fock space point of view, Phys. Rev. B 104, 024202 (2021).
- Roy and Logan [2021] S. Roy and D. E. Logan, Fock-space anatomy of eigenstates across the many-body localization transition, Phys. Rev. B 104, 174201 (2021).
- De Tomasi et al. [2020] G. De Tomasi, S. Bera, A. Scardicchio, and I. M. Khaymovich, Subdiffusion in the anderson model on the random regular graph, Phys. Rev. B 101, 100201 (2020).